Joint EM-Peds Conference Physcian Wellness and Resilience
Misuse of Adderall is a dangerous and under-estimated risk for students and residents who use this drug for test and work performance reasons. There is a serious risk of arrhythmia in persons using this drug. The risk is especially high in persons with structural heart disease. Dr. Bunney discussed a tragic case of fatal arrhythmia in a resident using Adderall as an alertness aid to work night shifts.
Most students and residents who misuse Adderrall get the drug from friends or it is prescribed by fellow residents. Do not use this drug unless prescribed for an accepted indication by a treating physician who is not a friend or family member and who is documenting the prescription and indication in a medical record.
Physicians make bad patients because we fear the loss of our identity as a healthy healer. There is stigma to being ill. We feel weak if we are sick. We don’t like being seen as a vulnerable person. We also have medical skepticism. We know the problems of the healthcare system and the errors that can occur. We are uncomfortable putting ourselves at risk in the healthcare system.
As physicians and healthcare workers, we need to look out for each other and care for each other.
Wellness=Longevity
Sleep hygiene matters for our health and nongevity
Take care of yourselves and each other.
*Casinos have learned that giving all their workers anchor sleep (sleep at some point during the hours of 1a to 6a) improves performance and longevity. Casino’s purposely schedule night shifts to change over at 4 am so that both night and day shift workers can get some anchor sleep during that 1a-6a time period.
As ER docs, bad things are going to happen to our patients and us. We need to have a spiritual anchor that’s get’s us through the tough times. We all need to find our own spiritual anchors.
Residents are at risk for burnout due to social isolation due to work demands. Residents tend to neglect their own emotional and health needs. Residents have limited control of their schedule. Perfectionism is a common trait of residents that can lead to burnout. Poor relationships with colleagues can increase burnout. Some residents may feel regret over their career choice. Anxiety over medical errors can lead to burnout.
As educators we need to teach residents and student how we have dealt with anger, anguish, grief, fear, failure, and other strong emotions that we have faced as physicians.
Dealing with stress: Anticipate your stressors. Interpret your feelings of stress as a sign or opportunity to take positive action to mitigate that stress. Believe in yourself that you can influence events and how you react to them. Talking about feelings and emotions can be very useful for lowering stress levels.
Dealing with stress in the moment: Take some time to remove yourself from a situation. Meditate with deep breathing. Rethink your strategy.
After the event practice self-compassion and think positive thoughts about yourself or do something nice for yourself or do something you enjoy.
Munoz/Naik Oral Boards
Case 1. 48 yo male with severe vomiting. Patient developed chest and abdominal pain. HR=116. BP=100/62. Patient has a history of pancreatitis. Patient was drinking the night before.
Diagnosis was Boerhaave’s syndrome. Patient’s pain was treated with IV morphine. IV fluid resuscitation was started. Broad spectrum IV antibiotics were also given. Surgery was consulted.
*CXR of Boerhaave’s syndrome. Look for mediastinal air. CT is more sensitive than CXR of course.
Boerhaave’s is a life-threatening disease and mortality is time dependent. Get patients to the OR emergently.
Case 2. 74 yo male with leg pain. Vital signs are normal. Patient has a history of CAD, DM, and vascular disease. He is a smoker. Exam reveals cool lower extremity with absent distal pulses. EKG shows Afib.
Diagnosis was ischemic limb from embolus. Treatment is with IV heparin. Patient also needs vascular surgery consultation. Be sure to consider other possibilities causing an ischemic limb such as dissection, thrombosis, and trauma.
Case 3. 3 yo male with temp of 38.9. Parents also note that patient has had fevers for 5 days. Child is well appearing on initial exam playing with toys. Patient also has conjunctivitis and rash.
*Kawasaki’s Disease Medium sized vessel vasculitis. (conjunctivitis, rash, palmar/plantar erythema, red/cracked lips/tongue, and lymphadenopathy). Consider Kawasaki’s in any pediatric patient with fever for more than 4 days.
Treatment for Kawasaki’s includes IVIG and ASA.
*Aneurysms secondary to Kawasaki’s disease
Katiyar Toxicology
TCA’s are the most common drug overdose responsible for ICU admissions.
TCA’s have a 3 ring chemical structure.
* Tricyclic Chemical Structure
*Tricyclic Overdose EKG. Note prominent R wave in AVR. Also EKG shows widened QRS.
Drugs with high volume of distribution have most of the drug in the tissue rather than in the plasma. TCA’s have a high volume of distribution Drugs with a high volume of distribution are not amenable to dialysis because the drug is predominantly in the tissue rather than the plasma and dialysis really only works on molecules in the plasma.
4 C’s of TCA overdose: Cardiovascular collapse, Coma, Convulsions, Anti-Cholinergic effect.
* TCA effects on the QRS predict the clinical severity of the overdose. Abhi also made the point that if the patient has persistent sinus tachycardia they may be more prone to arrhythmia and OBS/monitoring should be considered.
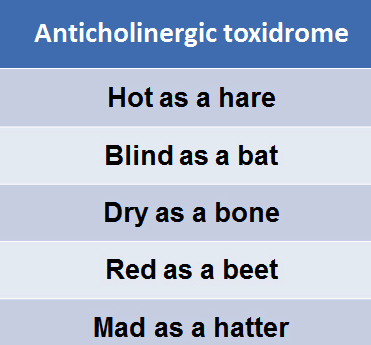
*Anti-Cholinergic toxidrome can be caused by TCA’s.
Treatment of TCA overdose: The antidote is Sodium Bicarb. Give 2 amps as a bolus then run a bicarb drip (1 liter of D5W with 3 amps of Bicarb added) at 250ml/hour.
Indications for bicarb are: QRS>120msec, Arrythmia, and hypotension.
Treat TCA-induced seizures with benzos and phenobarbital, third line is propofol.
Optimize electrolytes (K, Mg, Ca) to reduce the risk of torsades.
Avoid amiodarone(class 3 antiarrythmic) and 1a’s (procainamide) and 1c’s.
*Anti-arrythmic classification
Intralipid rescue may be useful for patients who are crashing despite the above management options. Finally ECMO is a last ditch move.
If patients who overdosed on a TCA are asymptomatic for 6 hours they are medically clear. If they have any cardiac or neurologic findings they should be admitted.
EDE Lightning Oral Presentation for SAEM
Hemorrhage after thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke.
HAT score Hemorrhage after thrombolysis.
*HAT Score
The HAT score performed moderately well predicting ICH after thrombolysis. In patients with high HAT scores you may want to adjust your risk assessment of intracranial hemorrhage upward when discussing TPA for stroke with patients and their families.
Jeziorkowski M&M
Know your equipment. Be sure you have the correct specimen collection swab or container before you collect the specimen. Make sure it is labeled properly before you go into the patient’s room.
With Code Strokes, consult everyone as early as possible. The time cutoffs for TPA and Invasive strategies come quickly in the ED. You have to push to get a timely CTA if indicated.
Possible ED Imaging decision making for stroke: Bad stroke (NIH stroke score>8) or devastating deficit (aphasia) get plain CT scan first. Consult neurology and interventional neuroradiology. If no ICH and patient within TPA window, start TPA infusion. Get CTA looking for large proximal clot. If CTA is positive patient may be candidate for interventional procedure.
Beware of framing bias. Just because patients are triaged as low acuity it doesn’t always mean they have a minor problem.