Denk/Traylor STEMI Conference
Case 1. Patient with chest pain. EKG showed elevation of AVR and diffuse ST depression.
2013 AHA Guidelines note that this is a STEMI equivilent. It can be due to left main, LAD, or triple vessel disease. Diffuse subendocardial ischemia from causes such as cardiac arrest or hypotension from blood loss, or sepsis can also cause this pattern.
You need to have this pattern recognition in your brain. Jenny and Logan presented multiple cases that were variations on this pattern. Not all patients went to the cath lab. ST elevation in AVR is a marker of increased mortality in both STEMI's and NSTEMI's. If you think the patient is having a STEMI with AVR elevation, (clear cut STEMI or patient is ill appearing or hypotensive or has acute heart failure) activate the cath lab. If you identify AVR elevation with diffuse ST depression in a patient who has other suspected diagnoses such as sepsis or hemorrhage or the patient is stable appearing, it was strongly recommended to emergently consult with interventional cardiology about cath lab activation.
Ahmed/Hawkins Oral Boards
Case 1. 3 mo infant brought in by parents unresponsive with no vitals. They found child not breathing in the crib and they started CPR. Resuscitation was continued in ED. Patient found to have a monomorphic VT and was defibrillated to sinus rhythm. Resuscitation required PALS management. Dosing for defibrillation is 2J/KG followed by 4J/KG if the first shock doesn't work..
Case 2. 19yo female with abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding. Vitals showed tachycardia and hypotension. B-hcg is elevated to 7500. FAST Exam shows free fluid in Morrison's pouch. Diagnosis was ruptured ectopic pregnancy and patient went to OR. Ampulla of the Fallopian tube is the most common site of rupture. Give RhoGam 50mcg to all RH negative women with a lost pregnancy in the first trimester.
In one study, only 10% of physicians were able to identify the presence of less than 400cc of free intraperitoneal fluid, suggesting that a positive FAST typically indicates a large amount of acute blood loss. The combination of positive FAST and positive pregnancy test should prompt an immediate call to OB-GYN to take the patient to the OR for a presumptive diagnosis of ruptured ectopic pregnancy. Bedside pelvic ultrasonography by emergency medicine physicians has led to improved time to diagnosis and should be performed whenever feasible. (CDEM Curriculum Reference)
Case 3. 49yo male with chest pain and diaphoresis 2 hours ago that resolved. Patient has hx of IDDM and HTN. EKG showed Wellen's syndrome.
Wellen's syndrome is associated with proximal LAD occlusion.
Wellens’ syndrome is a pattern of deeply inverted or biphasic T waves in V2-3, which is highly specific for a critical stenosis of the left anterior descending artery (LAD).
Patients may be pain free by the time the ECG is taken and have normally or minimally elevated cardiac enzymes; however, they are at extremely high risk for extensive anterior wall MI within the next few days to weeks.
Due to the critical LAD stenosis, these patients usually require invasive therapy, do poorly with medical management and may suffer MI or cardiac arrest if inappropriately stress tested.
Patient had further chest pain in the ED and repeat EKG showed acute anterior STEMI. Patient was taken to the cath lab.
Lovell Intellectual Wellness
First, An Overview of the other components of Wellness:
Social Wellness: Human interaction builds our resilience
Spiritual Wellness: We benefit from connecting to a belief system
Occupational Wellness: Finding purpose and meaning in our work
Physical Wellness: Get a doctor, sleep, eat well, exercise
Emotional Wellness: Conflict managment, narrative medicine
Intellectual Wellness: A commitment to life-long learning and skill acquisition.
Strategies for intellectual wellness: Read on ideas and topics outside of medicine. Try to alter your patterns of every day life, travel, audit a class, Khan Academy, Ted Talks, documentaries, learn a language, learn music, play games like euchre, experience something you don't understand like opera. You can take online college level courses with the website Coursera.
To enhance your intellectual wellness, start with a specific goal. Define what success will look like upon reaching goal. Set a timeline for meeting this goal. See if you can pair up with an accountability buddy. Somebody to help you stay on track. Set out to achieve the goal.
Naik ED Operations Update
Trushar discussed strategies for managing our boarding patients.
DeStefani HINTS Exam
3 components of HINTS exam: Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of Skew
Peripheral vertigo is a problem with the sensing organ, the vestibular apparatus. Central vertigo is a problem with processing movement signals in the brain.
Use the HINTS exam if a patient has acute vestibular syndrome. It is not helpful in patients with benign peripheral vertigo who have vertigo lasting less than a minute with change in position or halpike testing. Acute vestibular syndrome causes persisitent vertigo/dizziness lasting hours to days.
To meet the clinical definition of AVS, total duration must exceed 24 hours of continuous dizziness. This excludes most disorders in which dizziness typically presents with transient episodes lasting seconds, minutes, or hours, such as benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), cardiac arrhythmia, transient ischemic attack (TIA). Thus,these disorders rarely remain diagnostic considerations in AVS patients beyond the first few minutes or hours. Menière disease and vestibular migraine may be exceptions. (Newman-Toker Reference)
Head Impulse: When you move the patients head to the midline, if the eyes lag behind the head movement, that indicates peripheral vertigo.
Nystagmus: Unidirectional (fast phase of nystagmus is the same whether looking to the left or right) horizontal nystagmus is good and indicates peripheral disease. Vertical or direction changing nystagmus indicate central vertigo.
Test of skew: Have the patient fixate on your nose and then alternately cover each of the patient's eyes. If you see the uncovered eye adjust vertically that indicates a central cause.
Peripheral vertigo is identified by: eyes lag on head impulse, unidirectional horizontal nystagmus, and no skew.
There is a HINTS+ exam which adds hearing loss. Hearing loss increases the liklihood of central cause of vertigo.
We had a discussion of whether this test can be used reliably by ED docs. The studies that have looked at this test found a high percentage (@70%) of patients who had acute vestibular syndrome had a central cause. That percentage is high enough for most people at this lecture to OBS or Admit all patients with acute vestibular syndrome for neuro evaluation. Most people would be uncomfortable discharging home a patient based on HINTS testing.
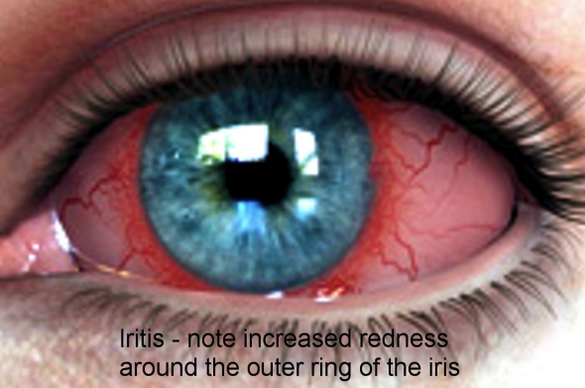
Logan Eye Emergencies
Ruptured globe with teardrop pupil
Iritis has redness most prominent around the limbus as opposed to conjunctivitis which has perilimbal sparing. Iritis is associated with sarcoid, TB and inflammatory bowel disease as well as multiple other etiologies.
Cirone mnemonic: Chlamydia is "clandestine" it takes longer to become evident on exam than GC.
Donapudi Pulmonary HTN and Pulmonary Fibrosis
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis is irreversible, with a high mortality and morbidity. Definitive treatment is a lung transplant.
Pulmonary HTN presents with very non-specific symptoms and signs. Look for signs of right heart failure. Lung sounds may be normal. EKG can show R side heart strain. CXR is nonspecific. LFT's may be elevated due to hepatic congestion. Pulmonary Function testing shows low lung volumes.
There are multiple categories of pulmonary HTN based on etiology.
In the ED get get all the usual cardiac labs and an echo. Correct hypoxia and hypercarbia. Use bipap if needed. Avoid intubation if at all possible. Intubation may result in very high PA pressures and cardiac arrest. Be cautious with fluids. Discuss with cardiology more specific management options.
We have a Pulmonary HTN Team at ACMC who can be paged for consultation on Pulmonary HTN patients.