Lorenz/Shroff STEMI Conference
Be very cautious giving IV beta blockers to patients with decreased cardiac function. Patients with diminished cardiac function can deteriorate with IV beta blockers. Determining a patient’s cardiac function can be challenging in the acute setting. Consider checking a bedside echo prior to giving a rate control agent. Start with a low dose and re-evaluate closely. During the discussion of this clinical situation, the Cardiologist at the meeting voiced a contrarian view and felt this was an overly cautious approach and that most patients can tolerate reasonable doses of rate control agents.
Tekwani comment: Get an ABG or VBG early on to see the lactate. It may clue you in to a hypoperfused state or cardiogenic shock. Harwood comment: A VBG also gets you a rapid potassium level.
Write here…
Cardiology comments: We try to avoid cath in patients with coronary artery dissection because cath can propagate the dissection. Most patients are treated with anticoagulation. I f a patient has a new right bundle branch block and left anterior fasicular block, be concerned for a proximal LAD occlusion and need for a pacemaker. Post-partum patients who develop coronary artery dissection should be counselled to not have further pregnancies. Cardiac surgery can be helpful at times to manage SCAD. There was consensus among the cardiologists that managing coronary artery dissections is very treacherous and cardiac cath is not a slam dunk. If you have a post-partum patient presenting to the ED with a STEMI you should activate the cath lab but discuss with the cardiologist the possibility of SCAD.
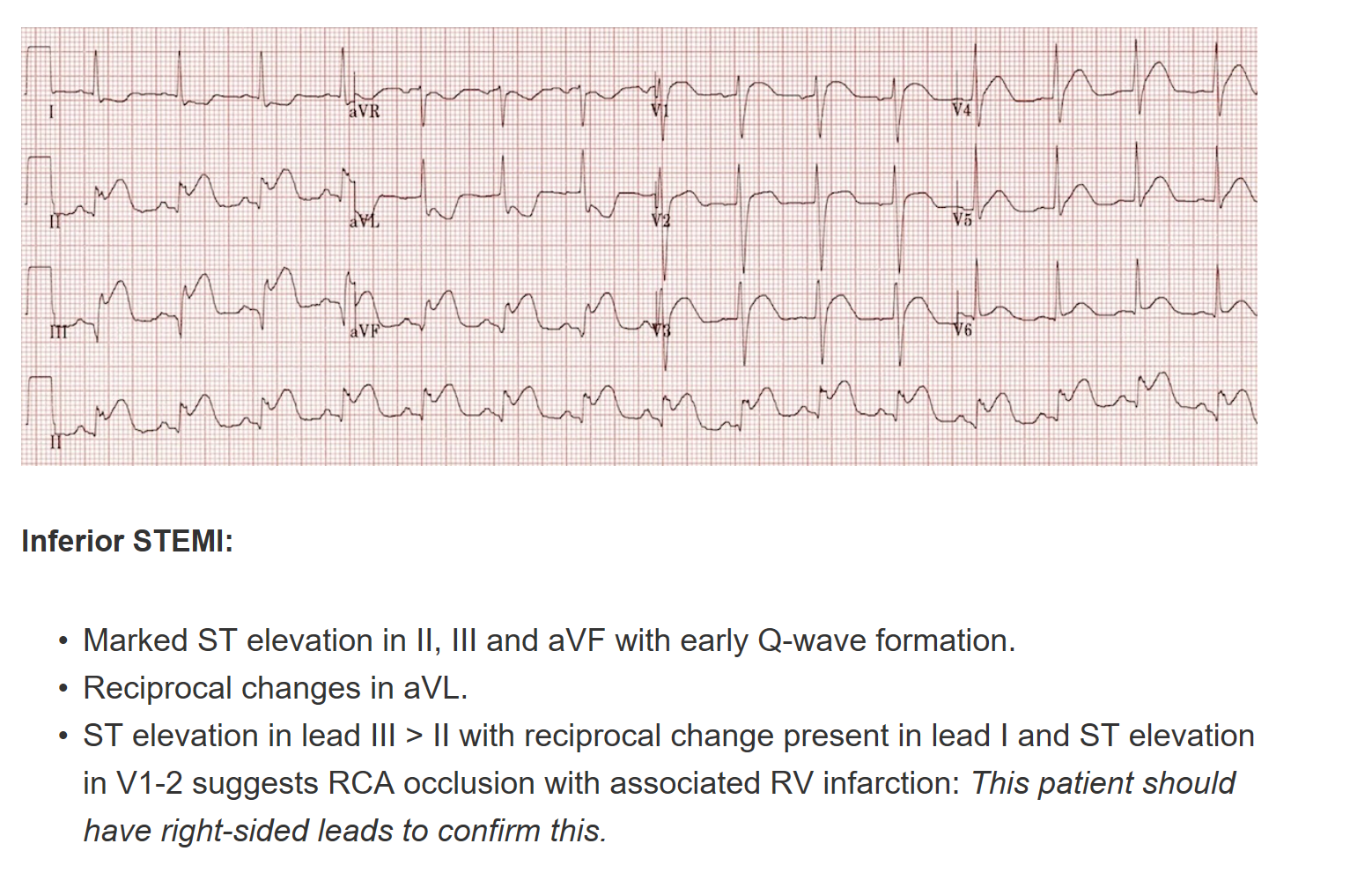
If you have concerns for ACS get repeat EKG’s every 10 minutes or so to try to pick up a STEMI. Inferior STEMI’s can initially have subtle inferior ST elevation, so be alert to ST depression in leads 1 and AVL which can be more eye catching. If Lead 3 is elevated more than Lead 2 or AVF it suggests right coronary involvement. Avoid Nitro in a patient with a normal BP and concern for right coronary infarct.
Felder/Tran Oral Boards
Case 1. 19yo female with chest pain for 2 days. Patient is tachycardic. Patient had been forcefully vomiting in the days prior to presentation.
Diagnosis was Boerhaave’s syndrome. Patient required IV antibiotics and Thoracic surgery consultation.
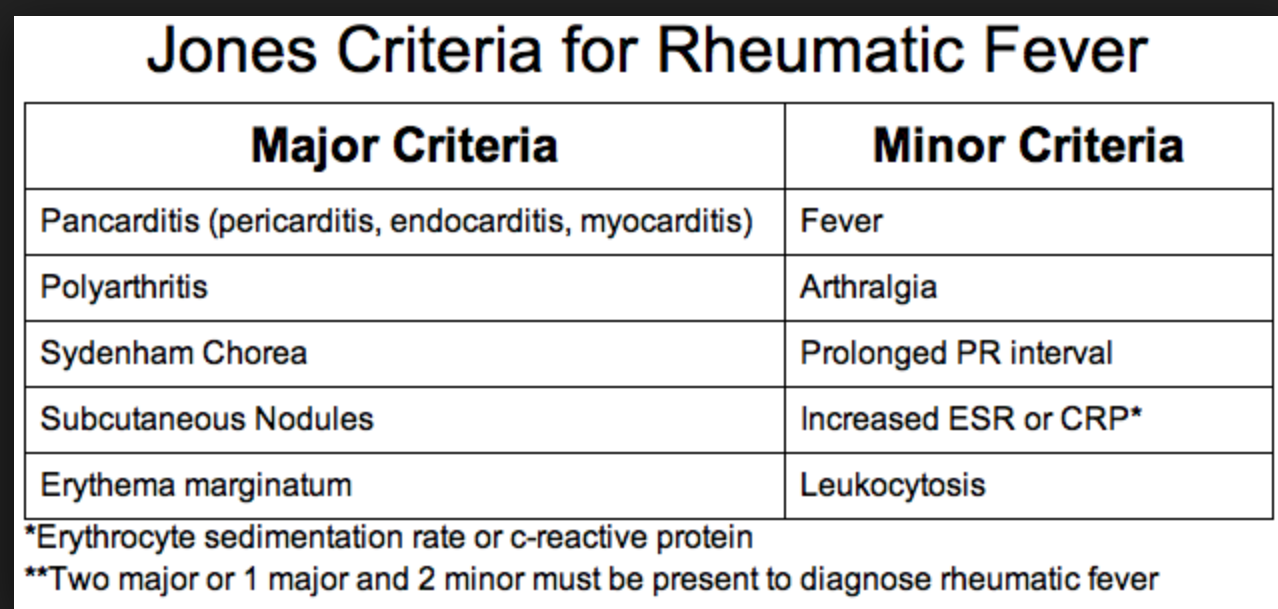
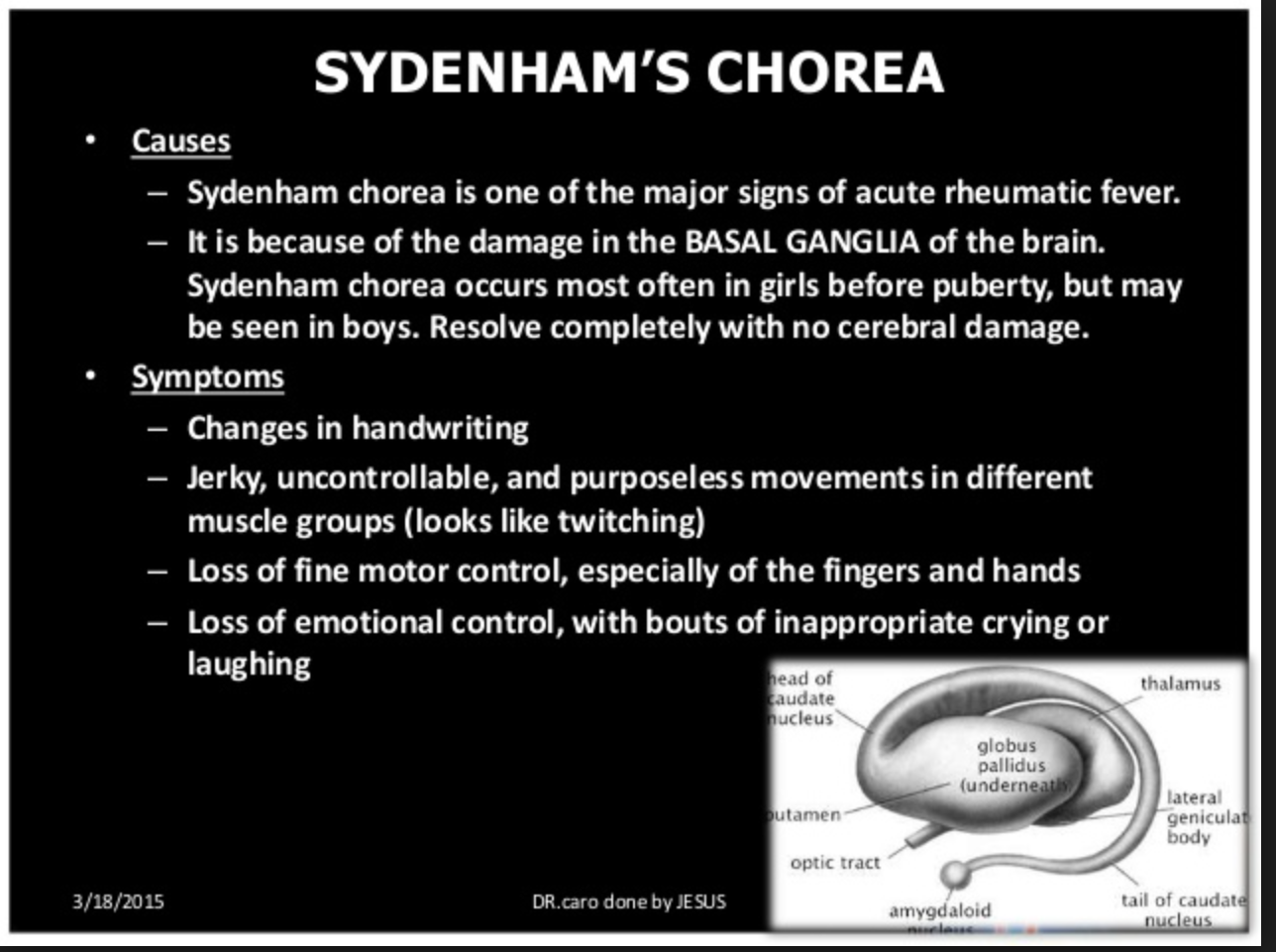
Case 2. 11 yo male with behavior changes. Vitals are normal. Patient had recent sore throat with incomplete antibiotic therapy. Patient recently moved from Saudi Arabia. Patient had choreiform movements and emotional lability. Diagnosis was Sydenham’s Chorea and Acute Rheumatic Fever. Treatment is 500mg of PCN BID chronically.
Sydenham chorea, which is due to an autoimmune insult to the basal ganglia,11 occurs in 10% to 15% of patients and may be the only manifestation of ARF; involuntary choreiform movements and facial grimacing are exacerbated by stress and disappear with sleep. Mild cases may present with restlessness and clumsiness. The motor movements may be unilateral. Symptoms are often preceded by behavioral disturbances including emotional lability, personality changes, anxiety, and poor school performance. Some patients may have “Sydenham speech” that is characterized by bursts of dysarthric speech. The time to development of chorea (1–6 months) is longer than for arthritis or carditis: streptococcal antibodies may be decreasing or undetectable at presentation. Physical findings of chorea include irregular contractions of the hands when squeezing the examiner’s finger (milkmaid’s grip), spooning and pronation of the hands when the arms are extended, and wormian movements of the tongue upon protrusion. Alterations in handwriting may be noted. The duration of chorea varies, but it is a self-limited process. Recurrence has been reported in 20% to 60% of patients and usually occurs within 2 years of initial presentation.11 Sixty-three to 94% of patients with Sydenham chorea will also have cardiac involvement.11 (Tintinalli 8th edition)
Case 3. 64 yo female with facial weakness. Patient has DM and HTN. Exam also identified vesicles on the external ear and ear canal.
RAMSEY HUNT SYNDROME (HERPES ZOSTER OTICUS)
Ramsey Hunt syndrome is a herpes zoster infection of the geniculate ganglion. Signs and symptoms include unilateral facial nerve palsy, severe pain, and a vesicular eruption on the face. Ramsey Hunt syndrome may be indistinguishable from Bell's palsy if paralysis precedes the vesicular eruption. Cranial nerve VIII may also be involved with associated vertigo, nausea, and hearing loss. As opposed to classic Bell's palsy, when active herpes zoster is suspected, treatment is with both steroids (prednisone 1 milligram/kg per day PO for 7 days) and antivirals (famciclovir 500 mg PO three times a day for 7 days or valacyclovir 1 gram PO three times a day for 7 days).5 (Tintinalli 8th edition)
Tekwani Difficult Airway Conference
3 indications to Intubate: Protect airway, Can’t oxygenate or ventilate, Anticipated clinical course.
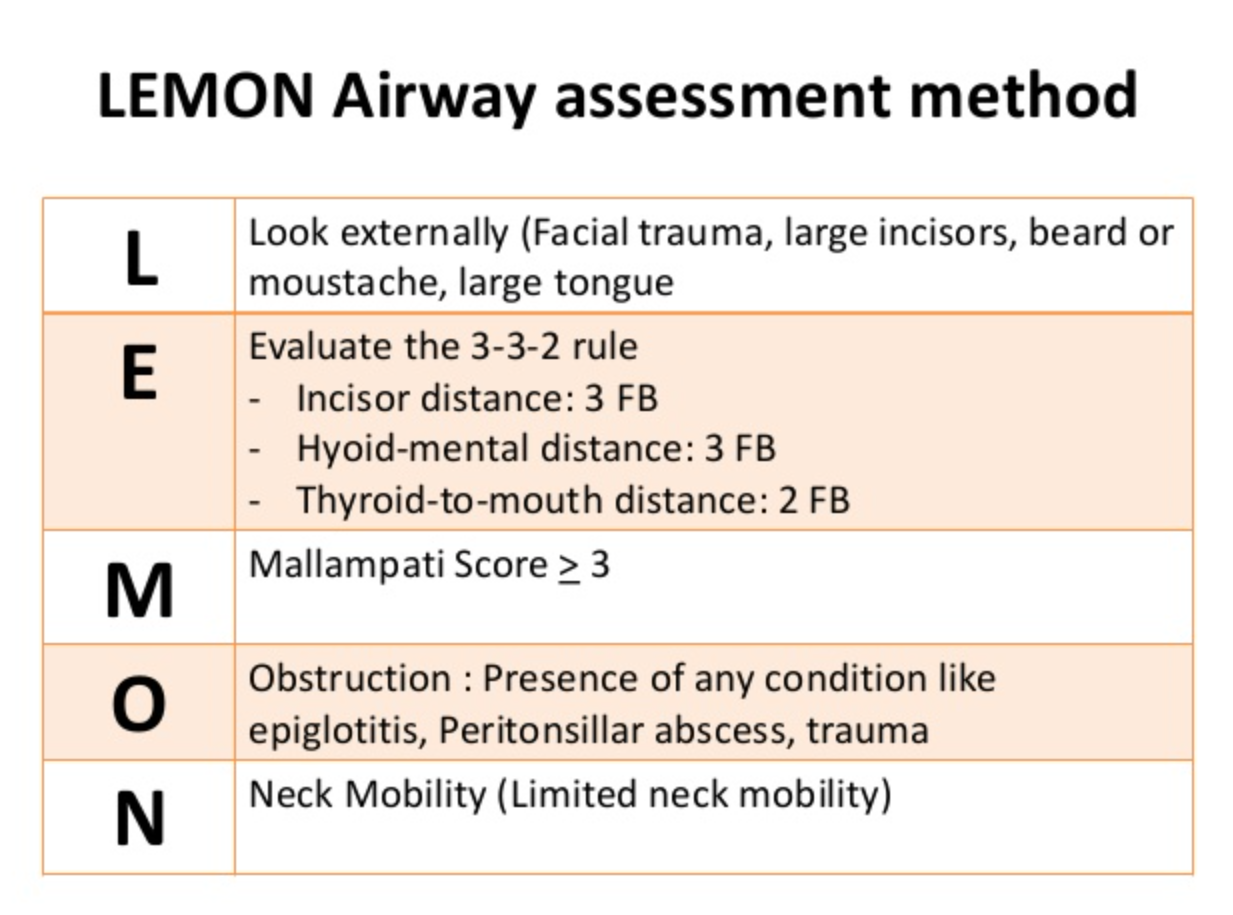
The LEMON mnemonic is a well accepted algorithm for the initial evaluation of the airway and predicting a difficult airway. It is not 100% sensitive for identifying a difficult airway.
Write here…
Thenar Grip Technique for bag-valve-mask
If you foresee a difficult airway, call for help. Ask Anesthesia or the MICU Intensivist to come down to back you up.
If you have a failed airway where basically you can’t intubate, place a LMA and proceed to cricothyrotomy.
Pre-oxygenate with NRB mask with O2 at “flush rate” for at least 3 minutes or use BIPAP. Preoxygenate the patient sitting up if possible to optimize pulmonary function. Also use apneic oxygenation at 15L NC in addition to your NRB or BIPAP.
Dr. Patel comment: You can use HI FLOW nasal cannula O2 for apneic oxygenation.
When intubating, start bagging the patient as soon as their O2 sat drops to the 95% range.
Case 1. If an asthmatic has a PCO2 of 42 or higher you need to be thinking they are fatiguing. You need to escalate care and be prepared for intubation.
After intubating an asthmatic patient set your vent to a Tidal volume of 6 ml/kg. Set ventilation rate at 12. Set O2 sat at 100% initially then titrate down to 40% quickly if possible. Set Peep at 0-5. I:E 1:5. High inspiratory flow rate 80-100 liter per minute. You will have to tolerate an elevated PCO2 so you don’t run into breath stacking, elevated peak and plateau pressures, or barotrauma.
Case 2.
ACE-I are the #1 cause of angioedema. Calcium channel blockers are the #2 cause of angioedema.
When giving ketamine for induction of a patient with a presumed difficult airway give 2mg/kg but give it slowly over a few minutes. If you give this dose rapidly, you can cause apnea.
Carlson Toxicology Case Conference: Antidotes
Antidote=Anything that improves survival from a toxin.
When calculating the Osmoles for a boards question you can simplify the equation by rounding 18 to 20, 2.8 to 3 and 4.6 to 5. You will get close enough to the right calculation.
Ethylene glycol and methanol will increase the anion gap. The antidote for ethylene glycol poisoning is fomepizole.
The antidotes for severe lead poisoning are BAL and EDTA. Oral succimer can also be used for mild cases or if you can’t use BAL due to peanut allergy. Editor note: mnemonic for BAL-EDTA is LED. BAL ends with L and EDTA starts with ED.
The antidote for Gyromitra mushroom poisoning is B6 (pyridoxine). Patients can seize from Gyromitra poisoning. B6 is also used for seizures due to INH poisoning.
The antidote for TCA cardiac toxicity is NA-Bicarb.
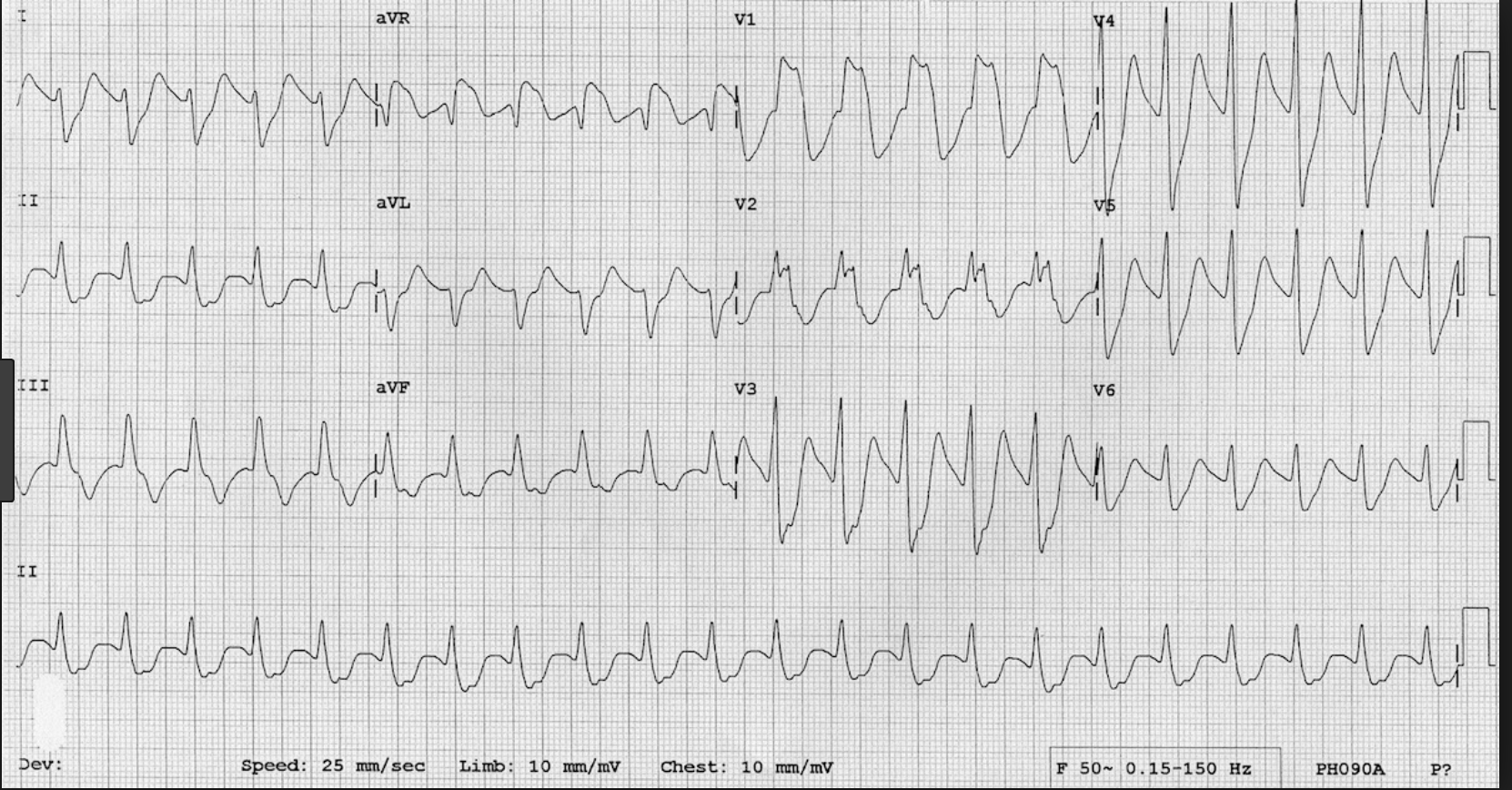
If you see this EKG in the setting of an overdose, think TCA and give a trial of NABicarb. If it works, it will narrow the QRS complex and narrow the terminal R wave of AVR. A Wide R wave in AVR and wide QRS complexes generally are clues on the EKG to a TCA overdose.
The antidote for calcium channel blocker overdose is Insulin at 0.5 U/kg bolus followed by 0.5U/kg/hr drip. You can also give calcium gluconate. Calcium gluconate is preferred over Calcium chloride due to less risk of soft tissue damage if the calcium extravasates from the vein.
Jimsonweed has anticholinergic effects. The treatment is benzodiazepines. A direct antidote is physostigmine if needed.
Antidotes for sulfonylurea overdose are glucose and octreotide. Glucagon may help if there is some glycogen stores remaining.
Oleander, foxglove, and lily of the valley are all botanical glycosides and the antidote for them is digibind (FAB fragments). You can also try atropine.
The antidote for hydrofluoric acid burn is calcium gluconate. The fluoride burns through tissue and binds calcium. You can give calcium gluconate by making a gel with surgilube, or give subQ injections with a TB syringe or for severe burns give intra-arterial calcium gluconate.
Methylene blue is the antidote for methemoglobinemia. Dapsone can cause methemoglobinemia.
The antidote for organophosphate poisoning is atropine and 2-PAM. The atropine reverses the muscarinic symptoms, specifically it dries secretions. 2PAM re-activates the acetylcholinesterase to stop the nicotinic effects.
The antidote for iron toxicity is deferoxamine. Side note by Dr. Carlson: The antibiotic omnicef is chemically similar to deferoxamine and can give small kids “brick red” poop. This can be concerning for parents.
The antidote for carbon monoxide is hyperbaric oxygen.