It seemed a shame to let the conference notes go while Dan took a well deserved break down under. So this week Christine Kulstad attempts to fill his shoes.
8am: King videoscope, King airway (laryngeal airway), and Ambu aScope training
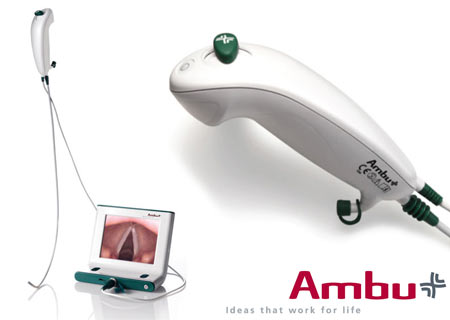
Ambu aScope- video cable (instead of fiberoptic) with articulating tip and cord to attach to video monitor (all disposable- everything except the monitor is disposable). When starting, keep video cable taut which helps function of articulating tip. Currently there is an oxygen port, next model will also have a suction port. Handle has on/off switch and lever that controls tip. Turn on monitor first- has 3 hrs battery life but should generally be charged. Pre-load ETT on tube stop at top of video cable, can go through nose or mouth. Remember when performing nasotracheal intubation, use a smaller tube (7-0). Consider pre-treatment with nebulized lidocaine and lubrication with lidocaine jelly, oxymetazoline (Afrin) spray or phenylephrine drops if time permits.
9:00- Tranexamic acid (TXA) and trauma- Rob Mokszycki (PharmD)
Trauma pts are coagulopathic due to multiple causes. During resuscitation, have to transfuse fluids (crystalloids), blood products (massive transfusion protocol potentially), and pro-coagulant agents (TXA and Factor VII).
TXA works by inhibiting plasmin and preserves platelet function.
First promise of TXA was in CABG- less blood transfusion, platelets functioned better, less blood loss. Same in spinal surgery.
CRASH-2 [Effects of tranexamic acid on death, vascular occlusive events, and blood transfusion in trauma patients with significant haemorrhage (CRASH-2): a randomised, placebo-controlled trial. CRASH-2 trial collaborators. Lancet. 2010 Jul 3;376(9734):23-32. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60835-5. Epub 2010 Jun 14.]
- international (except US) study of trauma pts and TXA. Outcome measure was all cause mortality. 2nd meausres- thrombotic complicatiosn, surgical intervation, transfusion. Inclusion- suspicion of bleeding within 8 hrs of injury, age >16. Exclusion- contraindication -active clotting, or allergy. 20,000 pts, groups well matched and low fall out. Injury severity was not measured. All cause mortality was decreased in TXA group. No difference in vascular occlusive events. Dosing not optimized- guesstimate from infusions given during surgery.
Secondary anaylsis of bleeding patients- benefit was greatest when given <1 hr, good if given 1-3 hrs, and negative if given >3 hrs. This was not a pre-specified subgroup.
NNT- 66 for all cause mortality. If this is true, could save 4000 lives in US.
MATTERs [Arch Surg. 2012 Feb;147(2):113-9. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.2011.287. Epub 2011 Oct 17. Military Application of Tranexamic Acid in Trauma Emergency Resuscitation (MATTERs) Study. Morrison JJ, Dubose JJ, Rasmussen TE, Midwinter MJ.]
- military retrospective trial- primary outcome mortality. 800 patients. TXA group was more severely injured than control, and overall group had more GSW and blast wounds. 48h and in-hosptial mortality were better in TXA group, more pronounced in massive transfusion subgroup. This study did find a higher rate of PE and DVT in the TXA group. NNT of 15, 7 in massive transfusion group. Time to TXA treatment and TXA dosage was not often recorded.
Summary- use TXA when <3 hrs and life threatening hemorrhage. Don’t use it if known clot. Possible harm in SAH cases (based on other studies).
Given in two 1 g doses, one as 10 min infusion and one as 8 hr infusion.
9:30- Student Loans- Jim Maletich
Medical school debt is increasing rapidly- median private med school debt is $180,000 and only $155,000 for public schools. Our residents owe from $84,000 to $450,000! As accrued interest is based on principal amount borrowed plus last years interest (capitalization), loan amounts continually increase. During residency, can be in negative amoritization- paying less than new interest accruing.
Deferment- grace period where you are not required to make payments. Usually capitalization does not occur during deferment.
Standard payment is your loan divided into 120 payments (generally about $2000/yr). Forbearance- don’t have to make payments but loans are all capitalized). EG- over 3 yrs capitalization adds $3000 to a $200,000 loan vs other fees and interest of $42,000.
Federal Repayment Plan for subsidized loans (IBR- income base repayment)- payments cap at 15% of discretionary income (your income – 150% of poverty limit[$11,490]) which ranges from $0 and $500/month. Government pays your interest so your interest does not capitalize. 3 year limit.
Consolidation- federal option- save 0.25 to 0.5% interest. Private option loses subsidized perks.
Public Service Loan Forgiveness- Must work for tax-exempt 501(c)(3)- federal, state, local, or tribal government for 120 monthly payments (residency counts). Then they repay the rest of your loans. Question if funding will exist by the time you qualify.
10- Admin Study Guide Part 2- Chintan Mistry
Boarding increases LWBS rates, increases length of stay, and diversion rates.
Parental consent is required except for emergency treatment and EMTALA screening, reproductive health, emancipated minors (court order, married, pregnant, minor who is a parent, Armed Forces).
The medical screening exam required by law (EMTALA) checks for an emergency medical condition, does extend to patients in waiting room (no time frame given). Duty ends if patient voluntarily leaves without being seen (LWBS). If an emergency medical condition (EMC) exists, treatment must be provided. EMC means potential serious injury to patient or organ. Transfer the patient when risk of transfer is outweighed by benefits. EMTALA applies to all facilities that accept Medicare payment. EMTALA violation means fines not covered by malpractice insurance, and potential exclusion from Medicare payments.
In all 50 states, child and elder abuse must be reported- can be done by physician, nurse, or social worker. Don’t assume PMD will do it. You are protected legally when good faith reports made (someone may file suit, but they won’t go anywhere). GSWs and stab wounds are also reportable in all states.
For a malpractice suit to be successful, it must be proven that a breach of duty occurred (patient was in ED usually enough), actual injury did happen, standard of care was violated, and actions led to injury.
On call physicians can refuse transfer of patient with an emergency medical condition when the receiving hospital does not have the capacity to accommodate the patient. Capacity means facilities, expertise, and space.
Leaving against medical advice (AMA)- the treating physician determines if they are competent to make that decision. It’s nice to have a refusal form on file, but it isn’t necessary and doesn’t help much legally. Alternative care should be provided to patients leaving AMA, and discharge instructions should be given. In a teaching setting, the attending should be involved- also don’t let your nurse do it without your involvement. It IS good to have your nurse witness your discussion and document it independently.
1030- Dialysis- Abraham Thomas
Nephrology update- can do dialysis for ED patients without requiring admission (can be done in ER, SUU, and HD unit). Call nephrologist early for potential discharges who are missing HD so that it can be rescheduled.
Good practice to check access site, ask about dry weights, dialysis schedule, dialysis center.
For HD patients who receive normal amounts of IV contrast for CT, they do not usually need immediate HD. It will increase their fluid balance by about 0.5 L. No good evidence it worsens anything, but caution may be beneficial for patients with temporary HD or improving renal function.
Gadolinium is contraindicated, but evidence of fibrosis was in patients who received multiple doses. If need, patients will need daily HD for 3 days afterwards.
BNP is not an accurate marker of volume status in HD patients- study shows some correlation with wide amounts of variation when studied in HD patients. However, a low BNP is probably accurate. Better to use clinical judgment to determine volume overload (dyspnea, RR, CXR, hypoxia).
Troponin can be elevated, but don’t ignore an elevated troponin. Change in troponin is more meaningful. Baseline elevation is not that concerning.
Please take down all bandages to look at access sites- especially intravascular catheters. Catheters are tunnels into IJ even though it looks subclavian. For AV grafts and fistulas- feel for thrill and listen for bruit. If it is not there, contact nephrology.
For bleeding vascular access (fistula or graft)- occluded artery for a minute or two. Then place mattress suture through skin ONLY at bleeding site. You can also use gelfoam or hemcon or similar. Bleeding is a marker of a problem with the fistula/graft so let nephrologist know even when bleeding is controlled.
Aneurysms can form at fistula/graft site. If you see firmness, skin turning white, or ulceration nearby be very concerned. This aneurysm is at high risk for rupture and vascular & nephrology should be contacted.
Acute kidney injury- creatinine increased by 0.5. ATN, obstruction, and pre-renal common causes. Always ensure pt is voiding (consider Foley), image kidneys with U/S or CT, check UA. Avoid NSAIDs, ACE/ARBs, contrast. When you have a patient with hyperkalemia, order repeat lytes in 4-6 hours.
Indications for HD- fluid overload; hyperkalemia, esp. with EKG changes; refractory acidosis; overdose- aspirin, lithium, toxic alcohols; uremia with encephalopathy/pericarditis
Chronic kidney disease- GFR <60 for at least 3 months. Usually from DM and HTN. These patients likely to present with volume overload, anemia, infection, hyperkalemia. Try to avoid pRBC transfusion in someone waiting for transplant as it will make a match harder. Don’t give these patients NSAIDs, gentamycin, or IV contrast if possible. If contrast necessary, give normal saline 1 ml/kg/hr for 6 hours pre/post. No benefit from bicarbonate or Mucomyst. Give instructions for creatinine check in 2-3 days.
Expect to see more kidney transplants at ACMC, we do them here. Call Dr. Chet Desai or Dr. Darshika Chabbra (417100), who are transplant nephrologists, surgeon is Dr. Mittal. Any change in baseline creatinine is critical. Any obstruction is potentially catastrophic. Evaluation after surgery- hematoma or urine leak. Afterwards worry about rejection and infection, drug toxicity. Make sure you check UA, BMP and levels of immunosuppresants which should be back in 2 hours. U/S likely helpful- specify that patient has a transplant.
Many causes of hyperkalemia- final common pathway through aldosterone which opens Na/K pump in tubule. Urgency of treatment depends on cause and clinical condition of patient- ie hydrating a patient who can urinate will lower K by itself.
Calcium-onset is immediate and duration is 30-60 minutes. Give 1 g of CaCl or Cagluconate over 2-3 minutes. Stabilize cardiac membranes.
Insulin/D50- insulin will push K into muscle cells, will drop 0.5-1.2 mEq. Onset in 20-30 minutes.
Bicarbonate- does not do very much. You can use it if pt is very acidotic (7.2 or lower) and you are putting them on a bicarb gtt.
Albuterol- safe and very effective. Must use 10-20 mg over 10 minutes. Effect seen in 90 minutes.
Kayexalate- exchange resin that may bind potassium but there have been cases of bowel necrosis. Do not use in pts with ileus, recent surgery, opioid use, bowel obstruction. Avoid multiple doses or large doses (30 mg OK). Onset in 90 minutes, lasts 4-6 hours.
If patients make urine, treat with IVF (saline) and loop diuretic (furosemide).
Peritoneal dialysis- most common ED presentation is peritonitis- happens about 1x/year/patient. May have all or only one of abdominal pain, n/v, cloudy dialysate. Work up as usual plus add 1 L of 1.5% dextrose dialysate, let it dwell for at least 20 minutes but ideally 60 minutes. Send for cell count and cultures. Peritonitis – 100 cells with 50% PMNs. Give vancomycin 1 g IP if possible, IV otherwise PLUS ceftazidime 1 g IV/IP or 500 mg ciprofloxacin bid. Can be discharged if not toxic and can be seen the next 1-2 days.
Hypercalcemia- treat levels 12-14 if symptomatic, all over 14. First, 200-300 ml/hr of normal saline. Do not had furosemide unless volume overload. Add calcitonin (4-6 IU/kg sq over 6-12 hrs x 48 hrs), bisphosphonate (ie zoledronic acid 4 mg iv over 15 min- slow onset but lasts for weeks).
1130- Amphetamines- Andrea Carlson
Pharmaceutical amphetamines-for ADHD, obesity (short term use), depression, enuresis, parkinsons (selegeline), alcoholism, narcolepsy.
Majority of drug abuse is misuse of drugs prescribed to patients, but illegal sales are rising. Check IDPH website before prescription refills of Adderall, etc.
Mild-moderate effects- agitation, hallucinations, HTN, tachycardia. Unlikely to have serious side effects from small, accidental ingestions.
Methamphetamines: 2nd only to cannabis in use. Significant geographical variation, seems to be increasing in Midwest. Highest rate of admission in all drug abusers, mostly psych. Crank is dirty, smelly meth. Yaba is meth + caffeine, big in Thailand.
Meth works by releasing norepinephrine and dopamine. Binds to serotonin receptors and effects brain glutamate. Renally excreted, large Vd. Causes neuroexcitation, tachycardia, HTN, mydriasis, hyperthermia, diaphoresis. Like cocaine but less dysrhythmias and seizure, lasts longer, more psychosis.
Meth- get horrible teeth. “Meth bugs”- from tweaking and picking at skin. Gross.

 Meth- increases child neglect and violence, HIV transmission. Montana meth project (now in 7 other states including Illinois) has been very effective at reducing use.
Meth- increases child neglect and violence, HIV transmission. Montana meth project (now in 7 other states including Illinois) has been very effective at reducing use.
Ecstasy (aka Adam, XTC, Molly)- often not in the pill (can be caffeine, designer drug, decongestants). Lower dose- trouble speaking, agitation, repetitive behaviors. Higher doses- more repetitive/compulsive behavior (bruxism), chorea, hyponatremia. Less cardiac effects. Chronic use- necrotizing vasculitis, psych problems.
Bath salts- cathinones- are newer congeners.
Drug screen- positive for a couple of days. Lots of false +- decongestants, buproprion, selegiline. MDMA and designer drugs false negative. Treat clinically.
Overall treatment- cool, calm room. Watch HR and core temp. Check BMP, CPK, EKG. CT head if seizure or significant CNS depression. Generous chemical sedation- up to 100 mg Valium (10 mg q 10 min). Can add anti-psychotics (newer generation). If sedated but still hypertensive, give phentolamine or nicardipine.
