Conference Notes 11-26-2014
Febbo M&M
35 yo female presents with hyperglycemia and left lower abdominal pain. Vital signs normal except tachycardia to 107. Physical exam showed left lower quadrant tenderness with no peritonitis. UA showed a few RBC’s and 1-5 WBC’s . CT Abdomen showed a kidney stone in the left ureter with some obstruction, hydronephrosis, and stranding. Patient’s pain improved with treatment in the ED and patient was discharged home.
The next day the patient returned with fever and tachycardia (SIRS). Blood sugar had increased. Patient was septic due to an infected, obstructed pyelonephritis. UA on second visit showed high WBC count and bacteria. Emergent decompression of the urologic tract was performed.
The 5 I’s for identifying the underlying cause of hyperglycemia: Infection, infarction, infant on board, indiscretion with diet or etoh, lack of insulin.
Indications for admission of patient with kidney stone : pain, single kidney, urosepsis, acute renal failure.
Infected hydronephrosis can be a difficult diagnosis. Lab testing is not always definitive. Pyuria should be present but can be minimal. Serum WBC is poorly predictive. Urine culture lacks some sensitivity and specificity.
Harwood comment: The obstructing stone in the ureter can block the downward stream of urine from the infected kidney and result in urine results that underestimate the severity of infection.
There are two options for decompressing the kidney: ureteroscopic removal of stone or IR percutaneous nephrostomy.
Brian went through multiple system issues that contributed to the difficulties with this case including: communication of vital signs from nursing to physician and difficulties with paging the consultants.
Harwood and Elise made the strong point that an infected, obstructed kidney can kill a patient rapidly. There was a discussion of how you could have picked up this diagnosis on the first visit. The initial urine study was not helpful. You have to look at vital sign changes, level of hyperglycemia, and the extent of ct findings. Elise and Harwood both stated that they are vigilantly looking for infected, obstructed kidneys with every kidney stone patient they see due to the lethality of this disease.
Sola comment: IR is more likely to drain the kidney during off-hours than GU consultants.
Harwood comment: If you are at a place where GU won’t come in urgently, call IR to treat the problem. If IR won’t come in then you have to call back GU and demand that they come in. If neither service will drain the kidney, then transfer them to a hospital that will. This has to get drained ASAP or the patient will die. Elise comment: IR is the better choice for drainage because these sick, potentially unstable patients don’t have to go to the OR.
Parker comment: The hyperglycemia on the first visit was a marker that there was an underlying infection. We don’t do a great job of identifying why diabetic patients are hyperglycemic. Emergency physicians must look for an underlying cause.
Harwood and Febbo both made the point that the stoic patient is a marker for serious underlying illness. Harwood has a low threshold for admitting stoic patients if he is unclear on their diagnosis.
Neal Lyons Update on Heparin Dosing Protocols
Heparin dosing protocols are based on intensity of heparinization desired.
Reduced intensity: No bolus and starting rate of 12u/kg/hr
Moderate Intensity (Cardiac reasons): 60u/kg bolus (4000u max) followed by 12u/kg/hr
High Intensity (DVT/PE): 80u/kg bolus (7500u max) followed by 18u/kg/hr
Beckemeyer Pattern Recognition
I am just including a limited sampling from this lecture. There were so many great slides/diagnoses.
FUGU poisoning from eating puffer fish. This is toxicity from tetrodotoxin. Supportive ventilation can allow patient to survive.
| Symptoms, Treatment, Decontamination |
|
| Syndrome Name |
|
| Symptoms |
|
| Onset of Symptoms |
Within 20 minutes to three hours |
| Rapid diagnostic assay |
None available. Sensitive chemical assays for tetrodotoxin have been developed but not approved for use. |
| Antidote |
None available |
| Supportive Care |
Artificial respiration to support breathing |

*Supracondylar fractures. Anterior humoral line should bisect the middle of the capitellum and it doesn’t in the xray on the left. The xray on the right has a relatively normal anterior humoral line. It still may be alittle anterior suggesting posterior displacement/fracture. Both films have evidence of posterior fat pads which is always abnormal and suggests fracture.
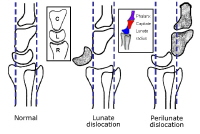
*Perilunate vs. lunate fracture
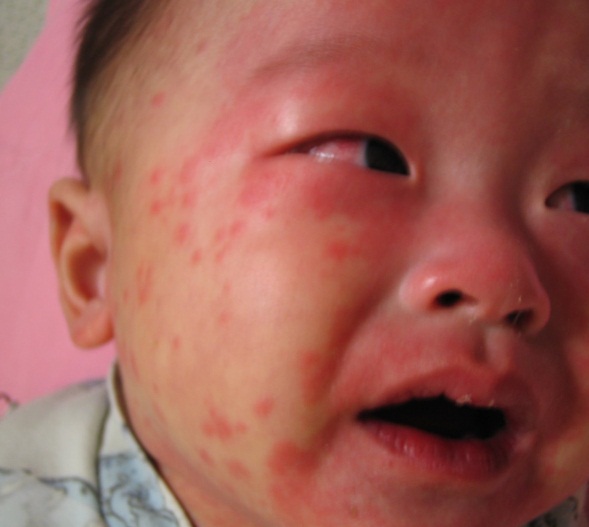
*Kawasaki’s syndrome
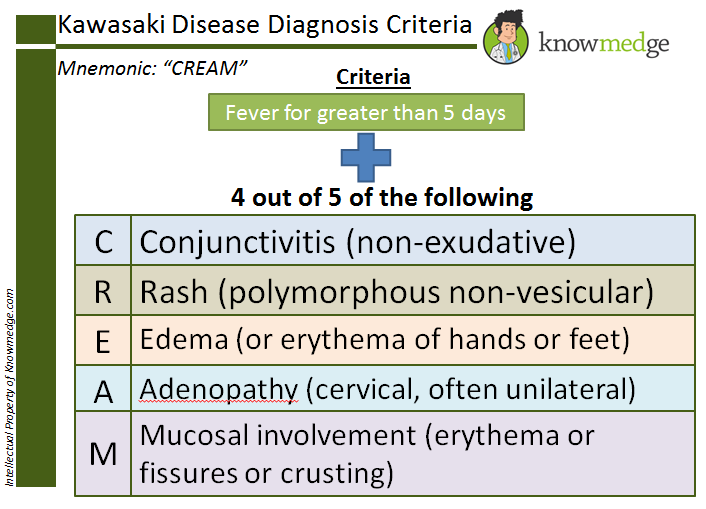
*Kawasaki criteria
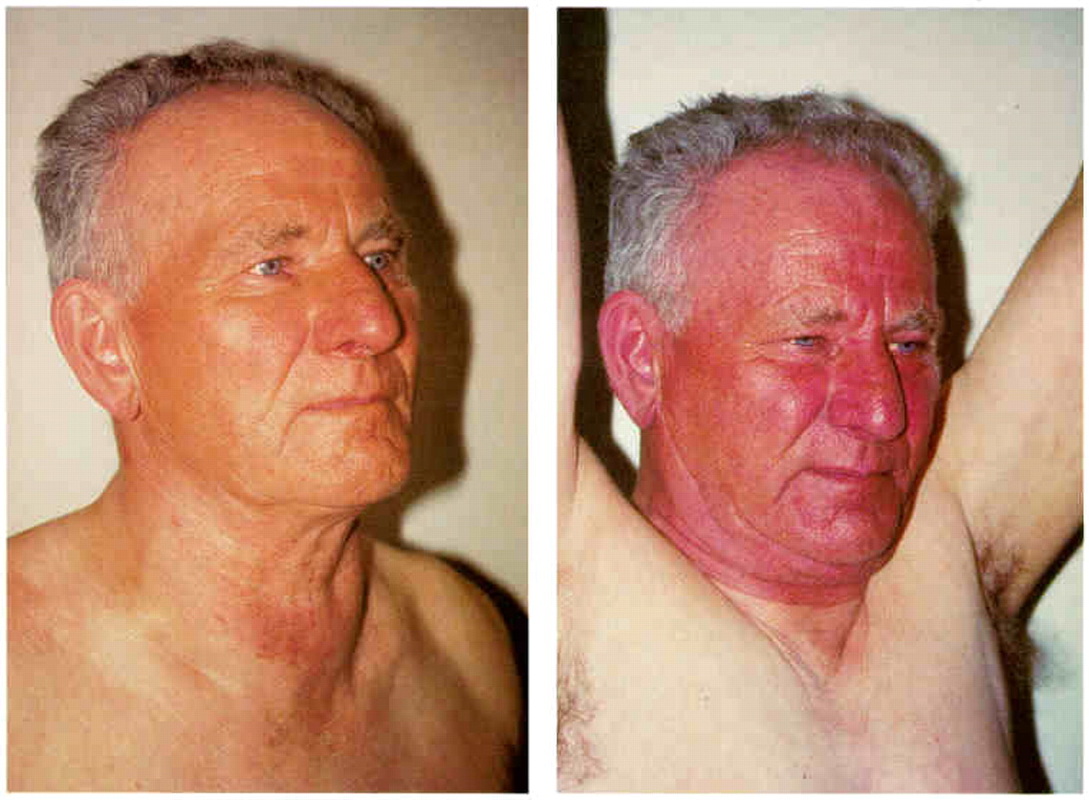
*SVC syndrome. Normal on left, plethora and swelling due to SVC on right. Usually due to a mass in the chest obstructing the SVC.
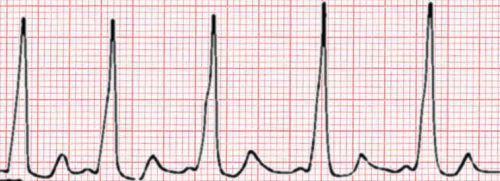
*WPW rhythm strip. Note the short pr interval, widened qrs with slurred upstroke
Meyers The Acutely Painful Joint
Is joint pain due to traumatic injury or not? If not, you have to consider infection, crystallopathy, and other things like RA, SLE, viral disease, and lyme disease.
Think septic joint in patients with acute onset pain, fever, immunocompromised patients, those with prosthetic joints and those with rheumatoid arthritis. Staph is the most common etiology. Inpatient mortality of septic joint is as high as 15%. One key exam point is pain with range of motion is 100% sensitive. If patient has non-painful range of motion they don’t have a septic joint. There are no absolute contraindications to arthrocentesis. Relative contraindications include overlying cellulitis and coagulopathy.
Arthrocentesis: Sterile procedure. Prep skin with iodine or chlorhexadine. Use a 16-18g needle. Use a bigger syringe for bigger joints. Smaller syringe for smaller joints. Larger syringes provide more suction and can accommodate a larger volume of synovial fluid.
For knee arthrocenteses insert your needle in the area of the superior lateral aspect of the patella.
John went through arthrocentesis approaches for other joints. Basically review your approach with a video or text prior to performing the procedure on a patient.
If the synovial fluid cell count is >50,000 this is considered more likely to be a septic joint. This cutoff is not perfect. There is significant overlap between septic joint and gout. There is data that a synovial fluid Lactate >10 is a strong indication of a septic joint. John tried to get a lactate level run on synovial fluid from taps he performed. He was unable to get lab or respiratory to run a lactate on synovial fluid here at ACMC.
Empiric treatment for suspected septic joint is Vancomycin. You also need to consult orthopedics for surgical washout or serial arthrocentesis Q 12 hours. Surprisingly, serial arthrocentesis works as well as surgical washout for septic arthritis.
Gout treatment: No NSAID is proven better than the other. So, use ibuprofen 800mg PO Q8 hours. If a patient can’t take ibuprofen the you can prescribe colchicine. Stop both treatments 2 days after symptoms improved.
There are risks to injecting local anesthetics or steroids into a joint.
Harwood comment: I don’t inject local anesthetics or steroids into inflamed joints after I drain them. Elise I will inject joints if the patient has had prior injections and it helped them. I don’t do it routinely.
If you get blood (hemarthrosis) on joint aspiration you have to be alert to the possibility of ligamentous injury, meniscal tear, or fractures of the joint line.
John discussed the orthopedic knee exam.
One nice comparison he noted was the warm-cool-warm vs. the warm-hot-warm exam. In general the knee should be cooler than the thigh and lower leg (warm thigh-cool knee-warm lower leg). In the inflamed or infected joint, the thigh will be warm-knee will be hotter- the lower leg will be warm similar to the thigh.
Harwood comment: Ultrasound can be very helpful in identifying joint fluid and improving your ability to drain it with arthrocentesis. My decision points are: Bacteria on synovial fluid analysis, patient comes in and gets started on IV antibiotics. WBC counts less than 25,000, patient usually goes home. WBC counts above 25,000 I will usually admit for further evaluation.
Harwood’s Gout cocktail: 1 dose of colchicine, 1 dose of decadron, and high dose ibuprofen. I stay away from Indocin due to it’s high side effect profile.
Burns Drowning Emergencies
500,000 deaths per year world wide.
Leading cause of death in kids in warm weather states.
Definition: primary respiratory impairment from submersion in a liquid medium.
Process:
There is voluntary breath holding for about a minute
When water gets in the throat there is reflex laryngospasm
Laryngospasm eventually relaxes
Active breathing of liquid
Hypoxemia
Lung injury
Neurologic damage
Management:
Pre hospital: ASAP give 2 rescue breaths then initiate ACLS
Provide O2
Cspine immobilization indicated only for significant blunt trauma
No Heimlich maneuver.
ED: Intubate or provide O2, Give PEEP
ABC’s
Perform nuero exam
Remove wet clothing
Order CBC, EKG, BMP, Utox, and ABG
CXR but it may not be predictive
CT head/cspine for blunt trauma
NG tube
Albuterol med neb treatments may be helpful
Ventilate with low TV and High PEEP
Arrange broncoscopy for sand or particulate matter in airway
Give volume if needed
Rewarm
Consider a seizure
No need for steroids or prophylactic antibiotics.
Prognosis: Markers for poor prognosis include longer submersion time, longer resuscitation time, warmer water, prolonged time to life support, GCS<5, continued CPR in ED.
Resuscitation should go on for at least for 30-60minutes. If it was a cold water drowning you should attempt resuscitation to at least 60 minutes. If the patient is hypothermic at one hour you need to rewarm the patient actively prior to pronouncing the patient.
Be very hesitant to pronounce drowning victims in the field. All drowning victims even of unknown duration should get a trial of resuscitation.
Elise comment: There is a big difference between kids and adults who drown in cold water. Kids cool rapidly and that better protects their brains and they do better than adults whose bodies/brains cool more slowly. Nevertheless, you have to take each patient on a case by case basis.
Harwood comment: I would do a CXR on all patients and observe them. If there is any abnormal CXR findings, I will admit the patient.
Schroeder/Negro Wellness and Nutrition
Traditional Low Fat diet philosophy: Avoid fat because it has the highest caloric density. In the 1950’s Ancel Keys presented research that touted the benefits of a low fat diet. This philosophy was incorporated into government guidelines. The food pyramid then became based on carbohydrates. The low fat diet has been the largest social experiment in history. In the US, a low fat diet has resulted in obesity. Sugar activates dopamine reecptors in our brain similar to cocaine/heroin. It also upregulates our hunger hormone receptors. Consequently with a low fat high carb diet you tend to eat more.
Our body is a finely tuned machine with a delicate balance of hunger and satiety hormones. Sugar messes up this balance.
If we change to eating more fat do we increase our risk of high cholesterol? There has never been any data showing increased cholesterol results in increased CV disease or mortality. If you want to focus on your lipids, lower your triglycerides and increase your HDL. The best way to do this is eat les sugars and live an active lifestyle.
Eat natural foods and avoid processed foods. Wild salmon, flaxseed, chia seeds, grass fed beef and bison and enriched eggs all are good sources of Omega-3 fats.
Decrease your omega 6 intake by watching your soy oil and vegetable oil intake.
Good fats to eat are medium chain triglycerides (coconut) and monounsaturated fats (olives, avocado, dark chocolate). When choosing dark chocolate, the darker the better and it should be in the un-dutched or non-alkalinized format. Williiamson comment: Dark chocolate should be at least 70% cocoa to get health benefits.
It is better to eat the whole food rather than just the oil or extract. For example eat the whole coconut, not just the oil.
Beets lower your blood pressure.
Potatoes and corn are not vegetables. They are grains.
Things that are not good for us: Less sleep, inadequate fluid intake, yoyo dieting.
Being active throughout the day is better than exercising. Exercising is just another way of depriving yourself of calories. Muscle building is the important for overall health. Muscle mass burns more calories and tends to keep you leaner.
Eat when you are hungry, eat enough protein, avoid simple sugars, eat vegetables with every meal throughout the day.
The less processed the food the better.