Tekwani/Pastore Oral Boards
Case 1. 28 yo female with right eye pain. Patient's child shot a nerf dart into patient's right eye the day before.
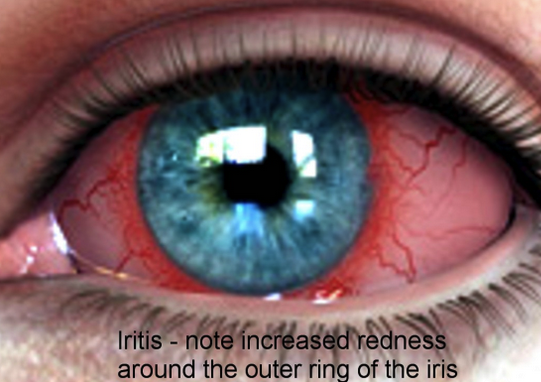
Traumatic Iritis with peri-limbal conjunctival injection. Be sure to evaluate for globe rupture, hyphema, and corneal injury. Always doucment visual acuity. Treat with cycloplegic drop. Discuss with ophthalmology about topical steroids. Some increased risk of glaucoma long term.
Case 2. 14 yo male with right knee pain for 2 weeks.
Patients with Osgood Shlatter's disease will have pain and swelling over tibial tubercle. Xrays may show apophysitis and widening of physis of tibial tubercle
Osgood-Shlatter disease is a traction apophysitis. The disease is self-limited. Treatment is NSAID's, ice and continued activity if pain can be controlled.
Case 3. Patient presents with a few days of fever and seizure. Patient is not immunized.
Koplik's spots with measles
Measles rash. Rash is preceded by fever and koplik's spots. Patient's with measles have T-cell suppression and can develop pneumonia and encephalitis.
It is critical to isolate patients with measles. The disease is highly contagious.
Harwood comment: 100,000 patients per year die from measles world-wide. It is a serious disease.
CDC Website snapshot of recent measles cases in US.
Usmani Abdominal Compartment Syndrome
Normal abdominal compartment pressure is 5-7 mm/hg
When abdominal compartment pressure goes up the patient will develop worsening renal function and oliguria.
Abdominal compartment syndrome is defined as an intra-abodminal pressure of 20 mm/hg or more with new organ dysfunction.
Abdominal Perfusion Pressure=MAP-Intra-abdominal pressure. Goal abdominal perfusion pressure should be above 50.
Obesity and pregnancy predispose a patient to abdominal compartment syndrome. This is because both obesity and pregnancy elevate the baseline intra-abdominal compartment pressure.
Other risk factors for abdominal compartment syndrome include: mechanical ventilation, sepsis, massive fluid resuscitation, liver dysfunction, laparoscopic surgery, SBO, and intra-abdominal infection.
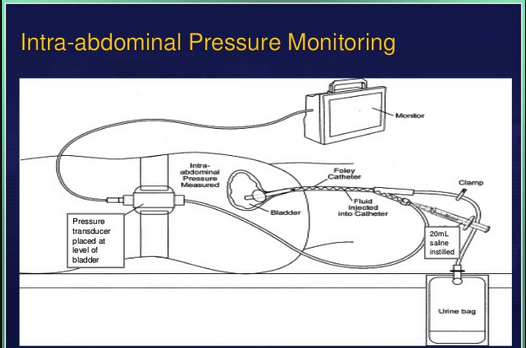
Physical exam of abdomen is not accurate in detecting intra-abdominal compartment syndrome. You need to diagnose abdominal compartment syndrome by measuring bladder pressure. This measurement is as sensitive as directly measuring the abdominal pressure with an intra-peritoneal probe.
Technique of measuring bladder pressure. Patient needs to be flat.
The kidney is the most sensitive organ affected by abdominal compartment syndrome. Patients will have decreased urine output and and rising creatinine. Pretty much every organ is adversely affected by abdominal compartment syndrome.
Mortality for abdominal compartment syndrome is 40%. Earlier diagnosis and decompression improves mortality.
Positioning patient's head/back at 20 degrees or lower optimizes abdominal compartment pressure. Positioning the head/back higher than 20 degrees increases abdominal compartment pressure.
Initially treat with NG tube, rectal tube, drain ascites if present, sedate and paralyze, avoid excessive fluid resuscitation, and position patient with head at or below 20 degrees. Lasix drip has no effect on intra-abdominal compartment pressure. Surgical decompression is the ultimate management of abdominal compartment syndrome.
Lovell comment: patients with ascites that is causing abdominal compartment syndrome can be treated initially with paracentesis. Paracentesis may or may not be definitive in these patients. Some patients may still need laparotomy.
We had a discussion of which patients in the ED we should be alert for possible abdominal compartment syndrome. The clinical picture is one of a critically ill patient, with worsening renal function, who has a lactic acidosis and low BP. Patients with ascites and/or liver disease who have received large volume fluids are at increased risk.
Burns/Denk Advanced Echo in the ED
TAPSE less than 1.7 indicates RV strain and suggests PE. To measure TAPSE, one must obtain an apical four-chamber view of the heart and use M mode to measure the longitudinal displacement of the lateral tricuspid annulus during systole and diastole. M mode will generate a sine wave that can be measured from peak to trough. Measurements less than 17mm are considered positive, suggestive of right heart systolic dysfunction and are associated with a poor prognosis in patients with PE, particularly in those with tachycardia or hypotension.
The TAPSE, a simple echocardiographic parameter, may help stratify risk in normotensive APE patients and is superior to RV/LV in MDCT and echocardiography. Patients with TAPSE ≤ 15 mm should be admitted to an intensive care unit and closely monitored. In these patients, acute PE may lead to clinical deterioration with indications for fibrinolysis. Subjects with TAPSE ≥ 18 mm form a low-risk group with good prognosis and are candidates for a short hospital stay. (Arch Med Sci 2016)
D Sign is seen on parasternal short axis view. An overloaded RV flattens the septum and makes the LV look like a D. This can be seen both in acute PE and chronic pulmonary HTN. This is a sign that may be easier to identify than TAPSE because it does not require m-mode measurements and can be identified by visualization alone.
There was a discussion of how to assess the RV pressure using echo. Unfortunately I don't know how to encapsulate it adequately for these notes. It starts with assessing the peak velocity of tricuspid regurgitation using an apical 4 view echo image. You then assess the variation of the IVC on a subxiphoid 4 chamber view while having the patient sniff. These two assessments can lead to a calculation of RV pressure.
Denk/Traylor Board Review
NIF and FVC can be used to assess respiratory status in patients with myasthenic crisis. Treat with myasthenic crisis with airway management if needed, IVIG, plasmaphoresis and steroids.
Low NIF and low FVC are indications for intubation in patients with myasthenic crisis.
6 Herniation Syndromes
Uncal herniation=blown pupil
Cerebellotonsillar herniation=pt is in extremis/dying
Subfalcine herniation=can't walk good/weak legs, bladder incontinence
Central herniation=forced downward gaze
Subcutaneous AICD/pacemakers in which the wires do not go transvenously but rather only in the subcutanous tissue were approved by the FDA back in 2012. They are becoming more common and used in patients with difficult venous access. The AICD/pacer device is placed in the left lateral chest wall. This patient's sternotomy procedure is separate and unrelated to the placement of the AICD/pacer.
Katiyar Toxicology
Most common cause of death from organophophate poisoning is respiratory failure from bronchorhea.
Small puncture wounds from Black Widow spider Bite. Patients will have sharp pain after bite. Patients can develop muscle cramps, hypertension, diaphoresis and anxiety. Patients can be treated with narcotics, benzos, BP management and consideration of antivenom. Update tetanus status. Patients can develop hypocalcemia but calcium administration has not been demonstrated to be effective in the management of black widow spider bites.
The only therapies with proven effectiveness are opioid analgesics and black widow spider antivenom. Antivenin Latrodectus mactans is an equine-derived antivenom based on immunoglobulin G.4,10,19,20 The proposed pharmacologic mechanism is binding of venom toxic constituents by the antivenom antibodies. A single vial (2.5 mL) generally provides adequate relief in human (adult or pediatric) poisoning cases.3–5,14,19,21 The Kaiser Permanente (KP) acquisition cost for one vial of Antivenin Latrodectus mactans was $27.71 in 2011. In the largest series reported to date of moderate to severe black widow spider envenomation (n = 163), patients treated with antivenom experienced a much shorter duration of symptoms and were less likely to be admitted to the hospital than those who did not receive antivenom.3 Relief of symptoms occurred within an average of 31 minutes of antivenom infusion.3 Administration of antivenom even late in the course of envenomation has been reported to be effective.21,22 In one reported case, antivenom was used effectively for the treatment of symptoms 90 hours after a black widow spider bite. (Permanente J 2011)
Black widow antivenom may be difficult to obtain. You likely will need to contact poison control to obtain it.
Ciguatera Toxin causes strange neurologic symptoms. The common buzz word for Boards is HOT/COLD sensory reversal. Treatment is supportive. Some references suggest mannitol improves symptoms.
Valproic acid toxicity causes prolonged QT interval and elevated ammonia level. Treat with L-carnitine.
The mechanism is too complicated for me, but basically carnitine administration helps the cell detox valproic acid.
On the left is methemoglobinemia, chocolate blood. For boards these patients will have a pulse ox of 85% due to the light wavelengths transmitted by the darker blood. Treat with methylene blue.