Conference Notes 10-29-2014
ACEP Week: Congratulations are in order to a number of our residents after a very successful ACEP conference!
Kasia Gore competed in the national finals of the Clinical Pathologic Case competition, giving an outstanding presentation on a case of epidural abscess.
 Lindsay Purnell, Mike Cirone, and Natalie Htet all presented research posters on Tuesday at the Research Forum.
Lindsay Purnell, Mike Cirone, and Natalie Htet all presented research posters on Tuesday at the Research Forum.
Natalie Htet ran for the EMRA Board.

Adam Bonder, Rachel Burt, and Katie Iannitelli received EMRA's largest award, the "Be the Change Award", for their work on ICU Boarders. This $5,000 award is granted to pursue a project designed to have a significant impact on emergency medicine education, research, practice or policy.
Terrific work everyone-our program and department are extremely proud of your hard work and success!!
Konicki Emoloyee Benefits
Best info resource is BENEFITS.ADVOCATEHEALTH.COM
Open enrollment is from 11-5 to 11-21 This is your opportunity to select/change your benefit options.
Login to advocatebenefits.com to select your benefits
Health Plans
EPO requires all your care to be at Advocate. If you go out of network you will pay more. It is the least expensive option.
PPO is least restrictive but most expensive. You can choose the doctors you see.
HMO You pick a provider and they decide on how you get your care.
Worst case scenarios: Your max out of pocket expense for all three health plans (for example you get hit by a truck)ranges from $11,000 (HMO) to $15,000 (PPO)
You really should do your Healthe You exam every year. Advocate gives you $600 cash benefit toward your health plan for doing this.
As part of Healthe You, there is a screening for tobacco use. If you use tobacco or you don’t get screened you will get a surcharge of $25 per pay period.
Hyatt Legal services is an option to have a lawyer on retainer. It is a low cost option to have legal services available if you need it.
Consider getting term life insurance from Advocate because it is inexpensive. It may be a god idea to get some life insurance while you are young & healthy. You can carry it forward if you leave Advocate.
The Advocate Dental and Vision plans are worth the cost if you see the dentist twice a year and if you wear glasses.
When deciding on 401K investments a simple rule is: pick the best performing funds over the last 12 months and don’t put more than 20% of your assets in any single fund.
- • Advocate matches your savings by contributing 50 cents for every dollar you save through the Plan, up to the first 6% of your eligible compensation. This matching contribution—which can equal up to 3% of your eligible compensation—applies whether you save
- • using pre-tax contributions, after-tax (Roth 401(k)) contributions or a combination of both
- • Vesting 20% of advocates contribution per year of service after 2nd year of eligibility (6 years = 100%)
- • Auto enrolled at 3% when hired
*Other Available Benefits
Paik Trauma Lecture
Poly-trauma patient with head and chest injuries.
The patient was resuscitated and bleeding from a scalp wound increased.
Doherty comment: It is common for bleeding to increase with resuscitation. That is why ATLS is now recommending only 1 liter initial crystalloid infusion instead of 2 liters. (so-called balanced resuscitation) Patients actually can bleed to death from severe scalp lacerations.
TBI: severe is GCS 3-8, moderate is GCS 9-13, mild is GCS above 13
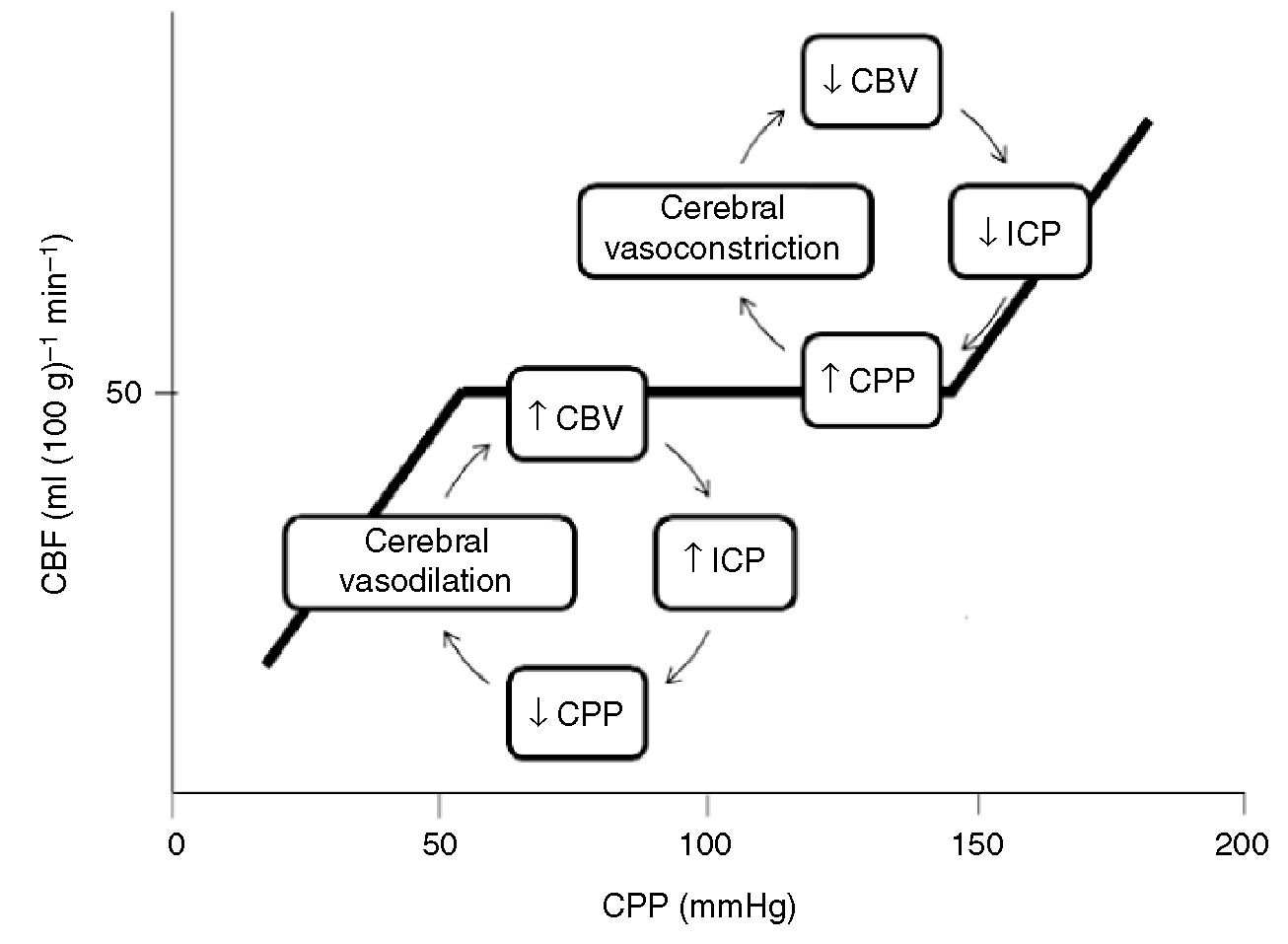
Normal ICP is <15 in adults.
*Cerebral autoregulation. Hypotension results in cerebral vasodilation and potentially increased ICP. Doherty comment: That’s why in trauma resuscitation, C comes before D. So if you have a patient with a blown pupil and hypotension from a ruptured spleen, you take them to the OR for management of the splenic injury. It is felt that the best treatment for the brain is to control bleeding and hypotension from the splenic injury.
Treat scalp lacerations initially with direct pressure. Use lidocaine with epinepherine for anesthesia as this will provide some vasoconstriction. Check for foreign bodies in the wound. Stitch or staple the wound as soon as possible. Update tetanus.
Doherty comment: If the skull is fractured and bleeding is coming from brain or intracranial vessels, stitching/stapling the wound won’t always help. Basically apply direct pressure, and get neurosurgery involved ASAP. Applying hemecon or some other hemostatic agent over the wound in addition to direct pressure may be helpful to control bleeding.
Doherty comments: Any open skull fracture should get IV and PO antibiotics to cover gram positive bacteria. Any otorrhea or rhinorrhea in the setting of head trauma should be considered a CSF leak and treated as a basilar skull fracture. Jim doesn’t do any testing of the fluid to confirm CSF leak. He recommends giving antibiotic coverage for CSF leaks again covering gram positive bacteria.
Epidural hematoma: Doherty comment: These injuries usually don’t have severe underlying brain injury. If the hematoma is evacuated within 4 hours, the patients do very well. This is in contrast to subdural hematomas which have significant underlying brain injury. Patient with subdural hematomas don’t do as well even if operated on promptly.
Regarding transfer of head trauma patients, Doherty did not recommend prophylactic intubation if the patient is alert and protecting airway and the transport time is not long.
Criteria for surgical evacuation of Subdural Hematoma
Midline shift >5mm
GCS drops by 3
Fixed dilated pupils
Hematoma >10mm
Diffuse axonal injury: Pt is in a coma and CT is normal. There is no specific treatment. Outcome is poor. Doherty comment: It is hard to prognosticate these patients. Some get better and some don’t. Improvement takes months. The injury is at a microscopic level diffusely. DDX in these patients is Toxicologic cause, DAI, or stroke.
ED Management of TBI: Hypotension and hypoxia increases mortality. Work to avoid both. Keep BP above 90 systolic and keep PaO2>60. Doherty: Aim for a Pao2 over 100. There is some data to support better outcomes with a PaO2>100. Harwood comment: Is the any benefit to pushing the PaO2 to >200 or 300? Doherty response: No evidence to support such high levels of PaO2.
There was a discussion of hyperventilation and the bottom line is don’t hyperventilate unless clear signs of increased ICP like a blown pupil. If you do hyperventilate, aim for a pco2 of 35.
If you use hyperosmolar therapy, hypertonic saline has the advantage of reducing ICP while at the same time expanding systemic volume. It is preferred over mannitol in the poly-trauma patient at risk for hypovolemia/bleeding/shock because mannitol will result in diuresis and potential further hypovolemia.
No role for steroids in the head trauma patient.
Give seizure prophylaxis for seven days in head injured trauma patients.
Tomasello (Visiting Professor/Alum)
Unfortunately I missed this excellent lecture.
Eastvold (Visiting Professor/Alum)
#1 Point of this lecture: If you see localized ST depression, keep looking for ST elevation. If you see localized ST depression it is a big clue to localized ST elevation somewhere else on the EKG. ST depression is often the most prominent sign of a STEMI.
If you see inferior ST depression and ST depression in the right precordial leads V4-V6 think subendocardial ischemia.

*Subendocardial ischemia (note inferior ST depression and ST depression in R precordial leads V4-V6 is greater than the left precordial leads V1-V3)
#2 Point When looking for ST elevation, compare the ST segment to the TP segment.
#3 Point The absolute millimeter criteria for STEMI will often fail you. It is the pattern of the ST segments that matters.
#4 If you see ST depression in V1-3 think posterior MI. More specifically, think posterior MI if you see horizontal ST depression in V1-3 that is greater than ST depression in V4-6 and upright T waves in V1-3. Confirm with a posterior EKG. Posterior EKG’s though are more specific and less sensitive than ST depression anteriorly. You can call a STEMI based solely on the anterior EKG findings for posterior STEMI.
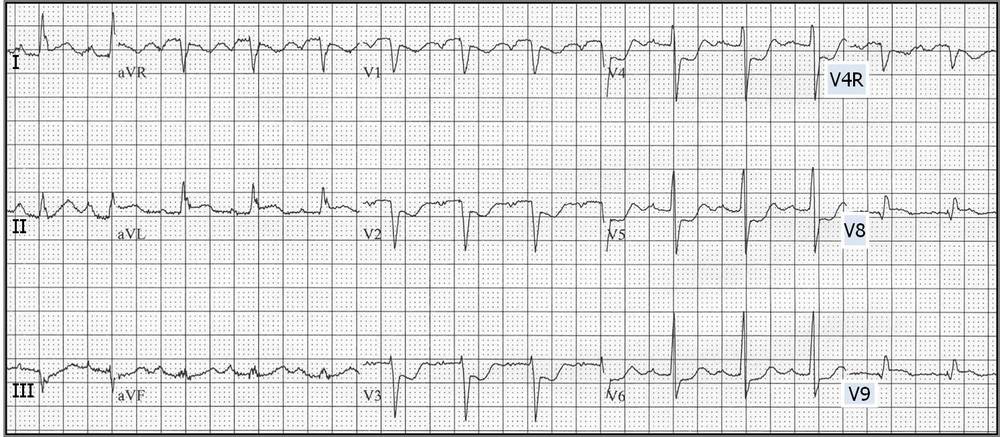
*Posterior MI (note anterior horizontal ST depression greater in V2 than V6 and upright T waves V1-V3. There are also posterior leads (V7-9)in this image which show ST elevation)
#5 If ST depression in V2 is greater than V6 think posterior MI. If ST depression in V6 is greater than V2 think subendocardial ischemia. Subendocardial ischemia can have isolated ST elevation in AVL and is still not a STEMI.
Isolated ST elevation in AVR is never a STEMI. If AVR ST elevation is greater than ST elevation in V1 that is more indicative of left main disease but is not a STEMI.
#6 If you see a new T wave inversion in AVL, look for an ensuing inferior STEMI. A new T wave inversion in AVL is a marker for developing inferior STEMI. Get serial EKG’s to watch for an inferior STEMI.
If you are unsure whether a STEMI is present, get serial EKG’s, get an echo to look for wall motion abnormality, and consult cardiology early.
#7 Benign early repolarization never localizes to the inferior leads.
#8 If ST elevation is greater in lead 3 than lead 2 think RV infarct. Avoid nitroglycerin in RV infarcts.
#9 New Tall T wave in V1 greater than T wave in V6 is indicative of an ensuing anterior STEMI/Proximal LAD lesions. The only exception is LVH with Strain pattern. That can have a tall T wave in V1 that is not ischemic.
# 10 50% of Anterior MI’s don’t have reciprocal changes.
Elise comment: Look at the ST segment contour as well. Straightening of the ST segment/loss of curve of ST segment indicates ischemia.
High lateral leads are 1, AVL, V6. They are contiguous leads.
#11 If the R wave in V3 and V4 is small think anterior ischemia.

*Anterior STEMI (hyperacute t waves) with small R wave in V3/V4 also no reciprocal changes which can happen in 50% of Anterior MI’s.
#12 Think PE if you see inferior and anterior T wave inversions and not in 1 and AVL.
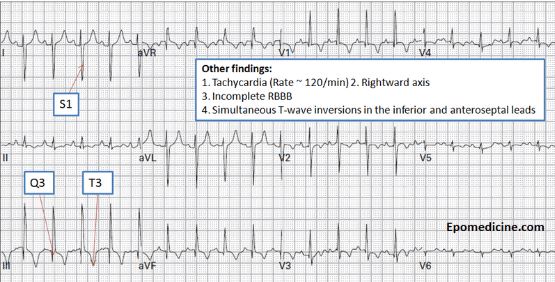
*PE EKG
Zimny Palliative Care Top 10 Pearls
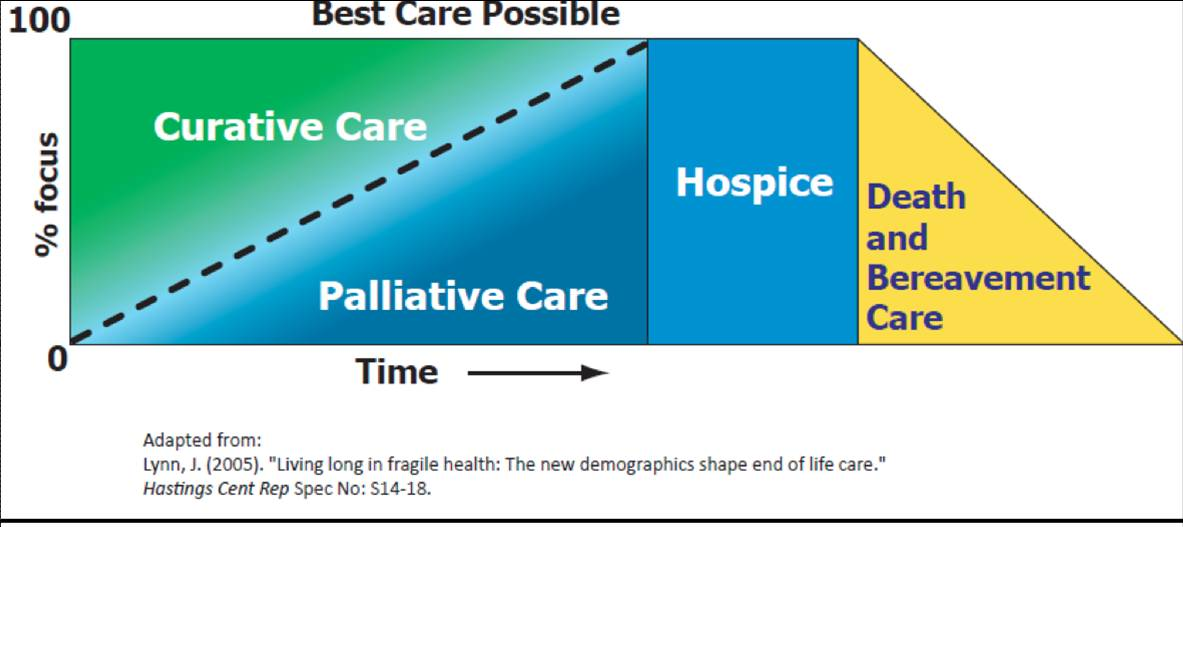
- Palliative care model has changed to begin palliative care earlier in the course of a potentially terminal illness. The level of palliative care increases as the illness progresses and standard medical care has less to offer the patient.
*Palliative Care model
Hospice is not a place, it is a model of care. Patients can be in Hospice at home. Hospice doesn’t always have to be revoked once a patient presents to an ED.
- DNR: The most specific meaning of DNR is when the heart stops beating, the medical team will not attempt to restart the heart. Once you have that decision made with the patient, then you move on to a discussion about whether the patient desires intubation, followed by a discussion about pressors and then painful procedures.
3. Pain management: Norco begins taking effect in 60 minutes and lasts 4 hours. So dosing is probably best Q4 hours. 2 norco=10mg Hydrocodone=10mg oral morphine= 3.3 mg of IV morphine. Starting weight based morphine dosing is 0.1mg/kg. Morphine is renally cleared. Hydromorphone and fentanyl are hepatic metabolized. Codeine is a waste of time. Codeine in most people is metabolized to morphine. However, not all people have the ability to metabolize codeine to morphine. Eastvold comment: There are also case reports of people who are hypermetabolizers of codeine and these patients can have respiratory arrest. So probably just don’t prescribe/order codeine. It has unpredictable effects.
4. Breaking bad news: SPIKES S=setting, P=perception (what are the family members’ or patient’s thoughts) I=invitation (ask the person if it is ok with them to break the bad news) K=knowledge (give the bad news, keep it short/easy to understand. You have to say the words died or dead) E=Emotions and Empathy (let the family express emotions and provide them empathy) S=Strategy and summary (end with informing them of next steps. Ask the person to repeat what they were told)
5. Constipation: Senna S is a good option because it has a stimulant and a softner. For more constipated patients give an osmotic agent like miralax. Opioid constipation can be treated with Senna S. Methylnaltrexone is a specific agent for opioid constipation as well. It does not cross the blood brain barrier. You have to get an x-ray first to make sure the patient is not obstructed. If there is an obstruction there is a risk of perforation with methylnaltrexone. Methylnaltrexone works within hours for patients with opioid related constipation to have a bowel movement.
6. Empathy Strategy: NURSE N=Name the emotion you are seeing. U=Understand Say I can’t imagine what you are going through. R=Respect the hard work that family members are doing to care for a family member. S=Support Say we will help you every step of the way. E=Explore what worries the person has.
7,8,9,10 We ran out of time.
Elise comment: How do you prognosticate for Alzheimer’s patients.
*7 Stages of Dementia