Denk/Traylor STEMI Confernce
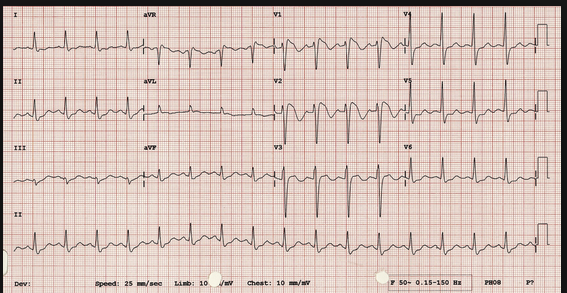
Inferior Posterior MI with RV involvement. Note the ST elevation greater in Lead 3 than Lead 2.
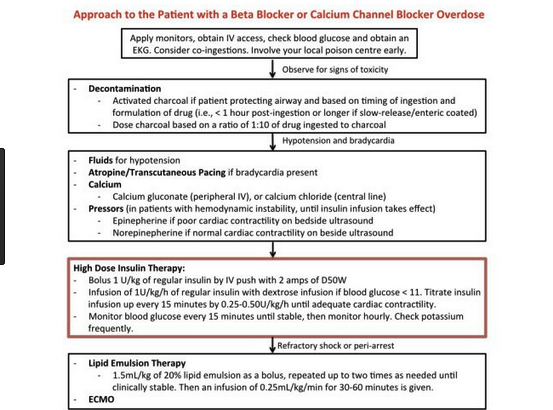
Patient with an Inferior/Posterior/RV MI. With hypotension. Cardiology advised initial 1 liter of saline. If that does not solve hypotension problem, next start a pressor. No difference in outcomes between dopamine and norepi. Dopamine has been shown to have more arrhythmia. Harwood comment: If the patient is bradycardic, dopamine has more chronotropy and is preferred. because you will raise the heart rate.
Editors comment: If the patient is not bradycardic, my reading of the below reference suggests that norepi may be the preferred choice.
New England JournalReference: The trial included 1679 patients with shock of all causes, of whom 858 were assigned to dopamine and 821 to norepinephrine. The baseline characteristics of the groups were similar. There was no significant between-group difference in the rate of death at 28 days (52.5% in the dopamine group and 48.5% in the norepinephrine group; odds ratio with dopamine, 1.17; 95% confidence interval, 0.97 to 1.42; P=0.10). However, there were more arrhythmic events among the patients treated with dopamine than among those treated with norepinephrine (207 events [24.1%] vs. 102 events [12.4%], P<0.001). A subgroup analysis showed that dopamine, as compared with norepinephrine, was associated with an increased rate of death at 28 days among the 280 patients with cardiogenic shock but not among the 1044 patients with septic shock or the 263 with hypovolemic shock (P=0.03 for cardiogenic shock, P=0.19 for septic shock, and P=0.84 for hypovolemic shock, in Kaplan–Meier analyses). De Backer N Engl J Med 2010; 362:779-789
Balloon pump therapyhas not shown a mortality benefit in cardiogenic shock but all the cardiologists present felt that ballon pumps are useful in supporting the patient in the short term. They usually use it in patients with high pulmonary capillary wedge pressure or patients who need improved coronary flow.
Editor's note: This feeling generally corresponds to a brief lit search on this topic. No overall mortality benefit but some patients did have hemodynamic improvement with balloon pump therapy.
Transvenous pacers are more easily placed in the cath lab than in the ED because of flouro. Only place a transvenous pacer in the ED if the patient is unstable due to bradycardia or heart block.
Factors making angioplasty more risky: If a patient has prior CABG it makes angioplasty much more difficult. Patients who have had cardiac arrest prior to going to the cath lab have worse outcomes overall. When in a difficult decision making situation regarding whether or not to take a patient to the cath lab, be sure to document the collaborative decision making that you had with the cardiologist. Lovell comment: Your mantra should be "shared decision-making"
Polycythemia Vera can result in sluggish coronary flow and MI.
Regan Disaster Planning
The new paradigm after the Columbine event is to extricate victims as soon as possible. Most SWAT teams have tactical medics or doctors who go in with SWAT team to get shooting victims out as fast as possible and get them to medical care. This change has improved survival.
It is common for people to "freeze" and not react properly to a terrorist or mass shooting event. There are clear reports of this happening during the 9-11 event. First responders will need to give victims clear direction to get them to safety.
When EMS contacts the ED, key pieces of information include: are there pediatric patients involved, is there a HAZMAT component to this event, the number of victims, and the estimated time of arrival of patients to the ED.
If there is a disaster or terrorist or shooting event that affects our hospital a CODE TRIAGE will be called. The Emergency Operations Center (EOC) will be in the Conference Center Auditorium. Hospital Administrative personnel will run the EOC. We as ED physicians will provide triage and patient care. In a disaster the goal of patient care is not to provide "standard of care", but rather "sufficient care." Basically that means you provide basic stabilization care to patients, not definitive care.
"The term “altered standards” has not been defined, but generally is assumed to mean a shift to providing care and allocating scarce equipment, supplies, and personnel in a way that saves the largest number of lives in contrast to the traditional focus on saving individuals." AHRQ Publication No. 05-0043April 2005
In the event of a mass casualty incident, call the Medical Director of Disaster Medicine (Liz or Sean).
We then will huddle with ED nursing and physcian staff to assign duties.
There is a disaster box in the back charting room. It has written role cards for staff. Doctors will assigned to Triage (1 physician and Charge nurse in the ambulance bay) or to Treatment of patients. Both attendings and senior residents will be treating injured patients. Junior residents will take on the role of moving our patients already in the ED out of the ED to make room for the injured patients.
Physicians report to the Charge MD who will be Sean, Liz or the most senior ED physician in the ED.
The Trauma Surgeons will be in the OR's.
Triage will occur in the ambulance bay. Treating physicians in the ED will stabilize patients and identify which patients require the OR as soon as possible.
Use IO access preferentially in a disaster situation. DO NOT spend the time to place a central line or ultrasound guided line.
Employ your Trauma skills to stabilize patients: assess/protect airway, use needle thoracostomy/chest tubes to treat pneumothorax and hemothorax, give blood, use TXA liberally, control extremity bleeding with tourniquets, get patients to the OR.
Additional physicians who are called in should park in garages A,B, or C. When you get to the hospital report to the ED Administrative Offices.
Do not self-dispatch to the hospital in the event of a mass casualty incident. We don't want too many people here at one time. Only come in if you have been contacted to come in.
EM1's Pecha Kucha
Chinwala Sleep for EM Physicians
Unfortunately I missed this excellent lecture
Jurkovic Blessed
Heart warming lecture describing how senior residents have helped the interns learn and battle through adversity.
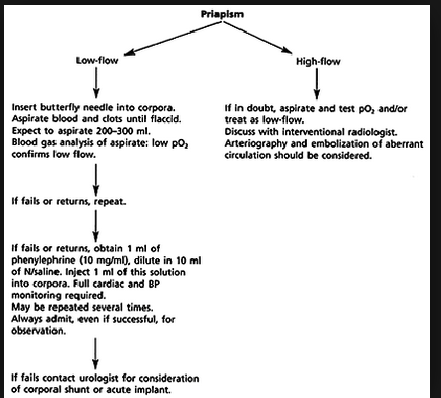
Pastore Priapism
Basic management approach to low flow priapism
Blood gas findings indicating low flow (ischemic) priapism
Low flow priapism is compartment syndrome of the penis. Give IV pain medication and perform a dorsal penile block. Aspirate blood from the corpus cavernosum. The blood will look like motor oil. Irrigate with saline. Inject phenylepherine . After detumesence apply an elastic bandage on the penis.
For priapism associated with sickle cell disease consult hematology for an exchange transfusion.
Kentor HINTS Exam
Used in patients with continuous vertigo for more than 24 hours. Is more reliable identifying a central cause of vertigo than MRI.
With rapid head turning, if eyes can stay on target then it may be central vertigo. With regard to nystagmus if has direction changing nystagmus or vertigal nystagmus that suggests central cause.
Kishi U/S Guided Forearm Nerve Blocks
Patrick described the procedure of using soft tissue ultrasound to identify and aid local injection around the median, radial, and ulnar nerves in the forearm .
Ohl Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
CT is close to 100% sensitive in the first 6 hours. Beyond 6 hours in the setting of a negative CT head, the next study would be LP.
Treat BP with Nicardipine. Keep the patient's head elevated at 30 degrees.
Vasospasm is more common in younger patients, smokers, larger bleeds, and patients with HTN.