Katiyar/Florek Oral Boards
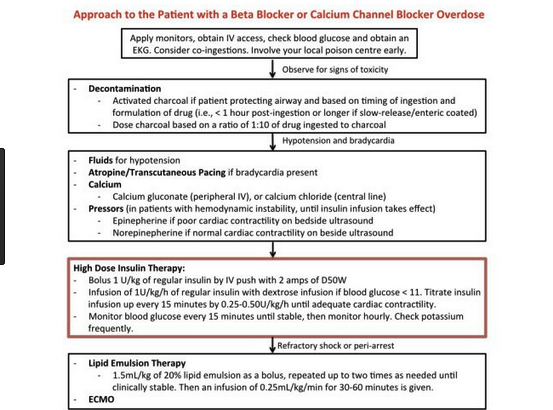
Case 1. 14 yo patient presents with 2 episodes of syncope on the day of her ED visit. The patient passed out while running in gym class. UCG is negative. EKG showed prolonged QT interval. Patient has history of depression and takes amitriptyline and sertraline. While in ED patient develops torsades.
QT interval 500ms or greater on EKG increases risk of Torsades. Treat torsades with defibrillation and IV magnesium 2g IV ( this dose can be repeated Q15min once or twice if still reverting to torsades) Once the patient is in sinus rhythm, you can use overdrive pacing or IV isoproterenol to increase the heart rate to 110-120 and narrow the QT interval. Next, correct hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia. You can give lidocaine or phenytoin as antiarrhythmics if needed beyond the other above measures.
Patient was treated with IV magnesium and defibrillation. She returned to sinus rhythm.
Defibrillation dosing in pediatric patients is 2J/KG initially followed by 4J/KG on repeat attempts at defibrillation.
There was a discussion about the optimal anti-arrhythmic in the setting of prolonged QT. The consensus was that you want to avoid Class 1A's like procainamide and Class 3's like amiodarone. They both can lengthen the QT innterval and cause torsades. 1B's like lidocaine are probably the safest choice.
Vaughan-Williams Classification of Anti-Arrhythmics
Case 2. 41 yo male with finger pain. Patient was working with "rust remover" to clean bricks. Patient was having pain due to hydroflouric acid exposure to hands. Treated with calcium gluconate gel.
Treat Hydroflouric acid burns with copious irrigation followed by applying a calcium gluconate gel made by mixing an amp of calcium gluconate with surgilube. Put that gel in a surgical glove and put it on the patient's hand. If the patient is still having pain, calcium gluconate can be injected into the subQ tissues with a 27g needle. Finally, if needed, calcium gluconate can be given intra-arterially. Consult with an Toxicologist and/or an Intensivist when considering intra-arterial calcium gluconate.
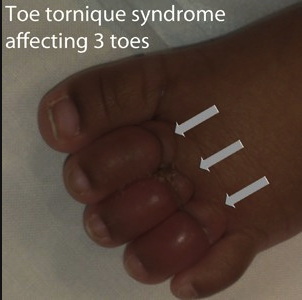
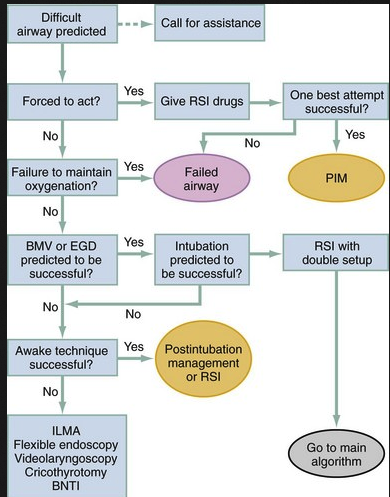
Case 3. 42yo male with back pain for one month since bicycle accident. Pain radiates down right leg. Pt notes some urinary incontinence. Pt states his belly feels full. On exam pt has diminished sensation and strength in right lower extremity. Patient had decreased rectal tone. Foley was placed to decompress the bladder. MRI showed compression of bilateral S1 nerve roots. Diagnosis was cauda equina syndrome. Patient was treated with emergent decompression surgery.
Clinical Picture of Cauda Equina Syndrome
Barounis/Jonas Central Line Workshop
The finer points of central line placement were discussed in this outstanding simulation workshop.
Traylor FirstNet Hacks Workshop
We were taught how to create our own order sets and dot-dot phrases.
Huu/Lorenz/Wing Thoracic Trauma
If you can resuscitate a penetrating thoracic trauma patient with ED thoracotomy, you have 90% chance of the patient surviving neurologically intact. Blunt trauma patients have low chance of survival from ED thoracotomy. If they do survive <2% have intact neurologic function.
If penetrating thoracic trauma with some signs of life, do an ED thoracotomy. If blunt trauma with no signs of life, don't do it. Every other situation is a case by case decision.
Emergency Department Thoracotomy
Published 2015
Citation: J Trauma. 79(1):159–173, July 2015
When placing a chest tube for a patient with thoracic trauma, put in at least a 32F size tube or larger.
A really obvious CXR demonstrating aortic injury
In summary, we propose three important and evidence-based recommendations regarding blunt thoracic aortic injury (BTAI), which were formulated using the GRADE methodology. First, we strongly recommend CT of the chest with intravenous contrast for the identification of clinically significant BTAI. Second, we strongly recommend the use of endovascular repair in patients with BTAI who do not have contraindications to endovascular repair. Finally, we suggest the use of delayed repair in patients with BTAI and emphasize that effective blood pressure control with antihypertensive medication must be used in these cases.
Blunt Aortic Injury, Evaluation and Management of
Published 2015
Citation: J Trauma. 78(1):136-146, January 2015.
Editor's note: There were better outcomes with delayed repair of blunt thoracic aortic injury for patients who required further resuscitation and/or management other life threatening injuries. In the subset of patients without other life-threatening injuries, delayed repair resulted in higher rates of paraplegia and renal failure.



























![Shimanuki et al [8] evaluated the clockwise “whirlpool sign” by color Doppler ultrasound in diagnosing midgut volvulus. In 13 patients with surgically confirmed midgut volvulus, color Doppler ultrasound showed clockwise “whirlpool sign” in 12 patien…](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55d5e97fe4b0c4913b06a4dd/1511367591796-HLSB2K15X45NLDXH8LJA/Snip20171122_10.png)