Lorenz Safety Lecture
You need to document a Face to Face evaluation when placing a patient in physical restraints. A face to face evaluation needs to be documented with 1 hour of placing a patient in physical restraints and then again at 16 hours if the patient is still in restraints. There is a ..facetoface template in FirstNet. The order for physical restraints needs to be renewed every 4 hours.
Advocate-wide, $40million dollars was not collected due to PTT, BNP, and urine toxicology tests. Insurance companies are not reimbursing for these studies if not clearly documented why they were necessary. If you order any of these 3 tests you need to document why the test was needed.
Logan/Schmitz Administrative Updates
Patients cannot be admitted to the detox unit from the ED. This is due to state regulations regarding the detox unit.
The new charting room has the new wide monitors for all the computers. All the computers in the new charting room have Dragon functionality.
Omari COPD
12% of Americans have COPD. It is a very expensive disease in human and financial terms.
25% of patients who smoke more than 15 years will develop COPD.
The severity of COPD is staged by spirometry. If you cannot exhale 70% of your lung volume in 1 second you have COPD. There are some experts who feel the 70% number should be varied based on age. Many persons over age 80 will not be able to hit the 70% number even though they never smoked.
3 cardinal signs of a COPD exacerbation are: acute dyspnea, increased sputum, and cough. Dr. Omari asks his COPD patients how long it usually takes them to resolve their COPD exacerbations. If it usually takes a few days then the patient likely will have a mild exacerbation. If they say they were in the hospital for a week or in the ICU the last time, you can expect a severe exacerbation.
Get the patient's O2 sat between 88-92%. You don't want to get too much over 92% to avoid CO2 retention. Watch out with continuous neb treatments. Nebs are driven by 12L O2 per min. If the patient is on the neb mask for more than an hour even if the neb has finished they are getting 12L/min of O2 and may start having increased PCO2.
Albuterol/Atrovent combo nebs are thought to be superior to albuterol alone for COPD patients. It is OK and may be better, to repeat the atrovent dosing along with albuterol nebs multiple times for COPD patients.
Dr. Omari's recommendation: For severe COPD exacerbations (speech with effort, accessory muscle use, diminished air movement on lung auscultation) give 125mg of Solumderol rather than PO steroids. After the initial 125mg dose of Solumedrol, he will then taper that down to 60mg IV Q6 hours. When they are better he will then switch them to PO prednisone. Harwood comment: If the patient is in the ED for more than 8-12 hours what is the second soumderol dose? Omari response: give solumedrol 60mg Q6 hours.
If a patient is coming to the ED for a COPD exacerbation, start an antibiotic. Give azithromycin or moxifloxacin. Azithromycin has an additional benefit of anti-inflammatory effects in addition to antimicrobial effect. For really sick patients, there is demonstrated mortality benefit for antibiotics for COPD patients going to the MICU.
Bipap has been shown to prevent worsening of an exacerbation and decrease intubations for COPD. BiPap=Good for severe COPD exacerbations.
We discussed a ballpark cut-off PCO2 where BiPap won't work for elevated PCO2. Dr. Omari said if the patient is responsive you can try BiPap up to somewhere around a PCO2 of 110-120. Levels higher than that or if the patient is obtunded you have to intubate because bipap therapy will not likely be successful in those patients.
For milder exacerbations (only 2 of the three cardinal signs dyspnea/cough/increased sputum), if the patient responds quickly to treatment in the ED and they feel they are back to their baseline breathing you can consider discharging home if they can get/take antibiotics orally, take oral prednisone, use an mdi, and have follow up in the next few days. If you can't get all that in place, admit or OBS the patient
Bonaguro/Chan Quality Updates
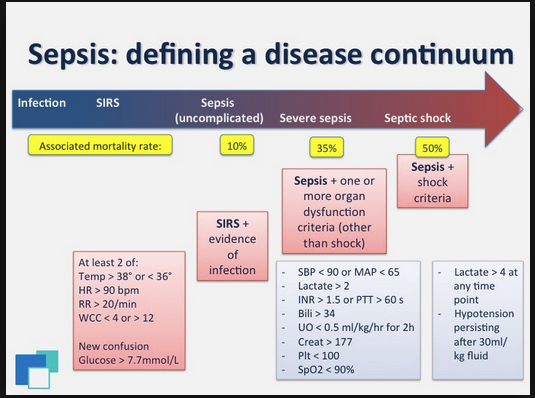
For Pediatric Sepsis Alerts, you need to call the alert overhead so nursing and PharmD's are aware that a Pediatric Sepsis Alert is in progress. You need to have antibiotics started within an hour. You need to have the fluid bolus administered within an hour.
If a child under 1 year of age has bilious emesis you gotta move fast to IV hydrate, consult surgery, and get an upper GI done to evaluate for malrotation with midgut volvulus.

























































































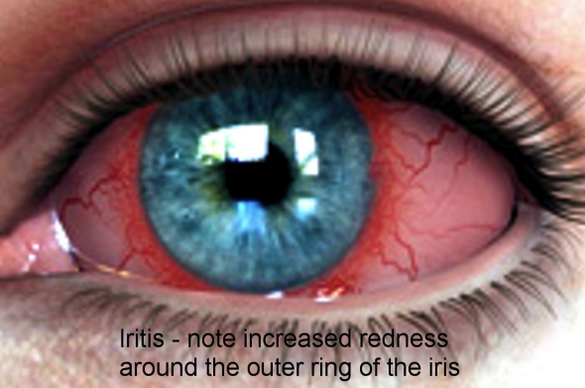






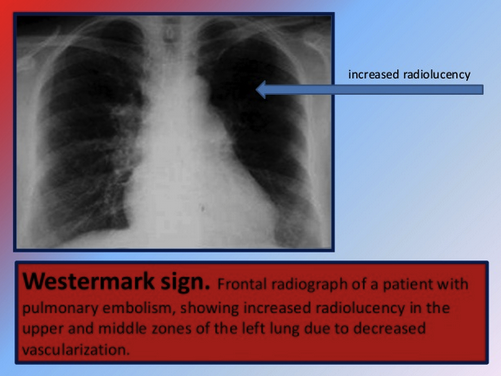
















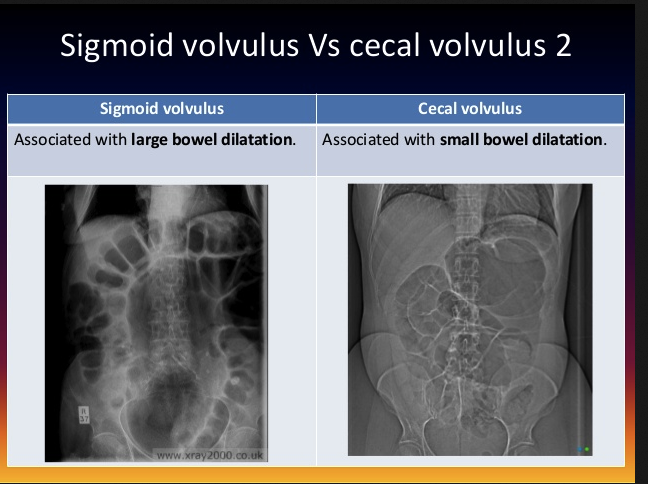
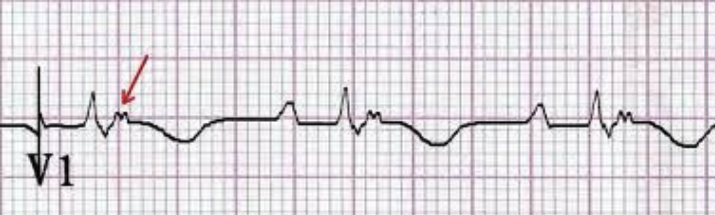




































![Shimanuki et al [8] evaluated the clockwise “whirlpool sign” by color Doppler ultrasound in diagnosing midgut volvulus. In 13 patients with surgically confirmed midgut volvulus, color Doppler ultrasound showed clockwise “whirlpool sign” in 12 patien…](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55d5e97fe4b0c4913b06a4dd/1511367591796-HLSB2K15X45NLDXH8LJA/Snip20171122_10.png)