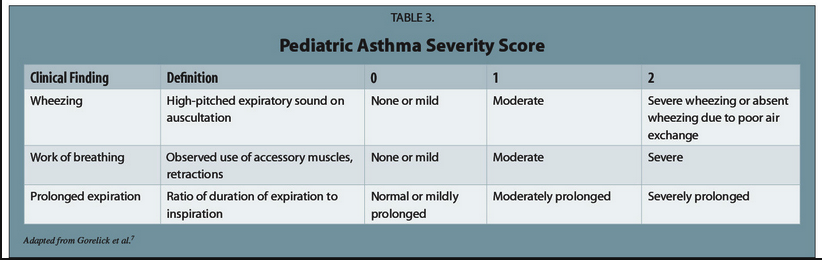
This Week’s Conference was our City-Wide Windy City EM Conference hosted at ACMC and organized by Dr. Andrea Carlson. It was a tremendous event! These notes capture just a small portion of the great info presented.
Regan Disaster Medicine and Emergency Preparedness
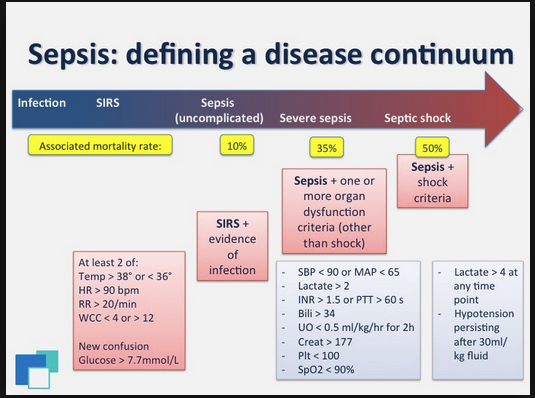
EMTALA is not relaxed during disasters or mass shootings. All persons who present to your ED need to be evaluated and stabilized.
Because of the chaos around a mass shooting and the fact that police respond before EMS, victims will come to your ED by cars, pickups, and uber. Victims also don’t just go to the Level 1 hospital. In Vegas, most people went to the Level 2 hospital because it was the closest and many people took an uber.
Hospitals need to be able to surge hundreds of patients to respond to a mass casualty event.
Rate limiting hospital personnel will be your anesthesiologists, intensivists, and pediatric surgeons. It is very difficult to have enough of these specialists available during mass casualty events.
Hospitals have run out of supplies like ventilators and chest tubes in mass shooting events.
Emergency physicians are the best prepared physicians to provide care in these mass shooting events. We have a key role to play in the response to mass casualty events.
Sharp Wilderness Medicine: Desert Endurance Racing
The emergency physician’s home environment is in the ED. We know how to manage emergencies in the ED. Moving out into the wilderness takes us out of our normal environment to care for patients.
If you are the emergency physician in an austere environment, if you can, you need to plan carefully for what you will need when you go out to that environment. The main concerns for persons in the desert are hyperthermia, dehydration, and exercise induced hyponatremia.
It can be difficult to differentiate dehydration from hyponatremia in the field.
Athletes need 500cc of fluid, 500mg of sodium, and 500cal per hour in the desert. It’s kinda the 500/500/500 rule in the desert. Like the 1/1/1 rule for massive transfusion.
Athletes in the desert, if they get hypoglycemic can actually have hypothermia in the heat. This is postulated to be due to the need for glucose to generate body heat.
Champus Sports & Event Medicine
Communication and Incident Command preparations are critical for large sporting events like a marathon.
The Marathon is a pre-planned disaster. Planners know that there will be a 2%-10% illness rate depending on weather. You also have to make sure the city’s EMS and police can function during the marathon so that you can get patients to the hospital who need that level of care.
The life-threatening diagnoses that planners have to be prepared for are cardiac arrest, hyponatremia and heat stroke.
The marathon planners have all the light posts numbered, they have observers on the course. They have a communication system to keep the whole system coordinated.
Mass sporting event planning can improve the overall resilience of the EMS system in a city and improve the city’s ability to respond to disasters.
McCombs EM in the Military Settings
All patients presenting to forward medical stations are searched for ordinance.
IED’s were devised by the Taliban to maim but not kill the initial soldier. So when the rescuing team came to extract the injured soldier a second more devastating bomb would trigger and kill the responders.
Nelson Addiction Medicine
Unfortunately I missed this outstanding lecture
Hawkins/Chan/Checkett/Mikkilineni Global Health Panel Discussion
If you want to pursue global health in your career, fellowship is probably the most efficient way to jump start that pathway. Fellowship allows you to more quickly build your global health skill set, get critical mentorship and develop a professional network.
If you don’t do a fellowship, the pathway forward the panelists all suggested was to network with people in the field. Go to a meeting and reach out to speakers. Follow up with an email to those networking contacts. Identifying where to invest your time with a global health organization is best informed by people you know or have made a contact with.
Senior Residents Around the City Memorable Moments in the ED
editor’s note: Each Senior Resident told a wonderful, memorable story that occurred in the ED. Some were funny, some were touching, some were clinically great diagnoses, and some challenged us to be mindful of our biases when caring for patients. The notes for this section only take one general point from each story.
When providing bag valve mask ventilation and you are not able to acheive adequate oxygenation try using a Peep Valve. It will recruit alveoli and may improve the O2 sat.
Sometimes giving people a kind gesture is all you can do in the face of an untreatable, life-threatening illness. That kind gesture can mean the world to the patient and their family.
Basics like bagging, cpr, intubation, hemorrhage control will save lives, even neonates. Focus on the basics and it will serve you well.
Cultural awareness can help de-escalate tense situations. Understanding the root cause of a patient’s fears and anxiety can lead to the best approach to caring for that patient.
An insect in the ear canal can be very very uncomfortable. Trust the patient if they say a bug is in their ear. Kill the bug with viscous lidocaine, then remove the bug with an alligator forcep.
Sometimes when we have a difficult case in the ED it may seem a downer at the time but a more useful perspective is to view it as a power boost/opportunity to improve our practice.
We belong. Our work as emergency physicians is vitally important. We are a team and we all care for each other.